What is an Operating System
Operating
System lies in the category of system software. It basically manages all
the resources of the computer. An operating system acts as an interface between
the software and different parts of the computer or the computer hardware. The
operating system is designed in such a way that it can manage the overall
resources and operations of the computer.
Operating
System is a fully integrated set of specialized programs that handle all the
operations of the computer. It controls and monitors the execution of all other
programs that reside in the computer, which also includes application programs
and other system software of the computer. Examples of Operating Systems are
Windows, Linux, Mac OS, etc.
An Operating
System (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware
resources and provides common services for computer programs. The operating
system is the most important type of system software in a computer system.
What is
an Operating System Used for?
The
operating system helps in improving the computer software as well as hardware.
Without OS, it became very difficult for any application to be user-friendly.
The Operating System provides a user with an interface that makes any
application attractive and user-friendly. The operating System comes with a
large number of device drivers that make OS services reachable to the hardware
environment. Each and every application present in the system requires the
Operating System. The operating system works as a communication channel between
system hardware and system software. The operating system helps an application
with the hardware part without knowing about the actual hardware configuration.
It is one of the most important parts of the system and hence it is present in
every device, whether large or small device.
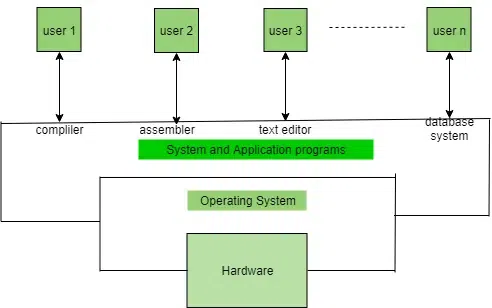
Operating System
Functions of
the Operating System
·
Resource
Management: The operating system manages and allocates memory, CPU time,
and other hardware resources among the various programs and processes running
on the computer.
- Process Management: The
operating system is responsible for starting, stopping, and managing
processes and programs. It also controls the scheduling of processes and
allocates resources to them.
- Memory Management: The
operating system manages the computer’s primary memory and provides
mechanisms for optimizing memory usage.
- Security: The operating
system provides a secure environment for the user, applications, and data
by implementing security policies and mechanisms such as access controls
and encryption.
- Job Accounting: It keeps
track of time and resources used by various jobs or users.
- File Management: The
operating system is responsible for organizing and managing the file
system, including the creation, deletion, and manipulation of files and
directories.
- Device Management: The
operating system manages input/output devices such as printers, keyboards,
mice, and displays. It provides the necessary drivers and interfaces to
enable communication between the devices and the computer.
- Networking: The operating
system provides networking capabilities such as establishing and managing
network connections, handling network protocols, and sharing resources
such as printers and files over a network.
- User Interface: The operating
system provides a user interface that enables users to interact with the
computer system. This can be a Graphical
User Interface (GUI), a Command-Line Interface (CLI), or a combination
of both.
- Backup and Recovery: The
operating system provides mechanisms for backing up data and recovering it
in case of system failures, errors, or disasters.
- Virtualization: The
operating system provides virtualization capabilities that allow multiple
operating systems or applications to run on a single physical machine.
This can enable efficient use of resources and flexibility in managing
workloads.
- Performance Monitoring: The
operating system provides tools for monitoring and optimizing system
performance, including identifying bottlenecks, optimizing resource usage,
and analyzing system logs and metrics.
- Time-Sharing: The operating
system enables multiple users to share a computer system and its resources
simultaneously by providing time-sharing mechanisms that allocate
resources fairly and efficiently.
- System Calls: The operating
system provides a set of system calls that enable applications to interact
with the operating system and access its resources. System calls provide a
standardized interface between applications and the operating system, enabling
portability and compatibility across different hardware and software
platforms.
- Error-detecting Aids: These
contain methods that include the production of dumps, traces, error
messages, and other debugging and error-detecting methods.
Objectives
of Operating Systems
Let us now
see some of the objectives of the operating system, which are mentioned below.
- Convenient to use: One of
the objectives is to make the computer system more convenient to use in an
efficient manner.
- User Friendly: To make the
computer system more interactive with a more convenient interface for the
users.
- Easy Access: To provide
easy access to users for using resources by acting as an intermediary
between the hardware and its users.
- Management of
Resources: For managing the resources of a computer in a better and
faster way.
- Controls and Monitoring: By
keeping track of who is using which resource, granting resource requests,
and mediating conflicting requests from different programs and users.
- Fair Sharing of
Resources: Providing efficient and fair sharing of resources between
the users and programs.
Types of
Operating Systems
- Batch Operating
System: A Batch
Operating System is a type of operating system that does not
interact with the computer directly. There is an operator who takes
similar jobs having the same requirements and groups them into batches.
- Time-sharing Operating
System: Time-sharing
Operating System is a type of operating system that allows many
users to share computer resources (maximum utilization of the resources).
- Distributed Operating
System: Distributed
Operating System is a type of operating system that manages a
group of different computers and makes appear to be a single computer.
These operating systems are designed to operate on a network of computers.
They allow multiple users to access shared resources and communicate with
each other over the network. Examples include Microsoft Windows Server and
various distributions of Linux designed for servers.
- Network Operating System: Network
Operating System is a type of operating system that runs on a
server and provides the capability to manage data, users, groups,
security, applications, and other networking functions.
- Real-time Operating
System: Real-time
Operating System is a type of operating system that serves a
real-time system and the time interval required to process and respond to
inputs is very small. These operating systems are designed to respond to
events in real time. They are used in applications that require quick and
deterministic responses, such as embedded systems, industrial control
systems, and robotics.
- Multiprocessing Operating
System: Multiprocessor
Operating Systems are used in operating systems to boost the
performance of multiple CPUs within a single computer system. Multiple
CPUs are linked together so that a job can be divided and executed more
quickly.
- Single-User Operating Systems: Single-User
Operating Systems are designed to support a single user at a
time. Examples include Microsoft Windows for personal computers and Apple
macOS.
- Multi-User Operating
Systems: Multi-User
Operating Systems are designed to support multiple users
simultaneously. Examples include Linux and Unix.
- Embedded Operating
Systems: Embedded
Operating Systems are designed to run on devices with limited
resources, such as smartphones, wearable devices, and household
appliances. Examples include Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS.
- Cluster Operating
Systems: Cluster Operating Systems are designed to run on a group of
computers, or a cluster, to work together as a single system. They are
used for high-performance computing and for applications that require high
availability and reliability. Examples include Rocks Cluster Distribution
and OpenMPI.
How to Check
the Operating System?
There are so
many factors to be considered while choosing the best Operating System for our
use. These factors are mentioned below.
- Price Factor: Price is one
of the factors to choose the correct Operating System as there are some OS
that is free, like Linux, but there is some more OS that is paid like
Windows and macOS.
- Accessibility Factor: Some
Operating Systems are easy to use like macOS and iOS, but some OS are a
little bit complex to understand like Linux. So, you must choose the
Operating System in which you are more accessible.
- Compatibility factor: Some
Operating Systems support very less applications whereas some Operating
Systems supports more application. You must choose the OS, which supports
the applications which are required by you.
- Security Factor: The
security Factor is also a factor in choosing the correct OS, as macOS
provide some additional security while Windows has little fewer security
features.
Examples of
Operating Systems
- Windows (GUI-based, PC)
- GNU/Linux (Personal,
Workstations, ISP, File, and print server, Three-tier client/Server)
- macOS (Macintosh), used for
Apple’s personal computers and workstations (MacBook, iMac).
- Android (Google’s Operating
System for smartphones/tablets/smartwatches)
- iOS (Apple’s OS for iPhone,
iPad, and iPod Touch)
FAQs on
Operating System
1. The
Operating System is which type of software?
(A) System
software
(B)
Application software
(C) Both a
and b
(D) None of
the above
Solution:
The correct
option is A, i.e., System software
2. Which of
the following is not an example of an Operating System?
(A) Windows
(B) Linux
(C) Mac OS
(D) MS-Word
Solution:
The correct
option is D, i.e., MS-Word
Windows,
Linux, Mac OS, all 3 are examples of operating system whereas MS-Word is an
example of application software.
3. Which
characteristic property prevents unauthorized access to programs and data?
(A) Security
(B) Data
Management
(C) Device
management
(D) Control
of system performance
Solution:
The correct
option is A, i.e, Security
Security
prevents unauthorized access to programs and data by means of passwords or some
kind of protection technique.
4. Which
characteristic property allocates and de-allocates the resources and also
decides who gets the resource?
(A) Security
(B) File
Management
(C) Device
management
(D) Control
of System performance
Solution:
The correct
option is B, i.e., File management
File
Management allocates and de-allocates the resources and also decides who gets
the resource.
5.
_____________ is designed in such a way that it can manage the overall
resources and operations of the computer.
(A)
Operating System
(B) File
Management
(C) Device
management
(D) None of
the above
Solution:
The correct
option is A, i.e, Operating System
The
operating system is designed in such a way that it can manage overall resources
and operations of the computer.
LastMinute Notes – Operating Systems
OperatingSystem Interview Questions
Learn more
about Different Operating systems here :


No comments:
Post a Comment