What is agile product management?
How do we define agile product management? It is a product
development philosophy that emphasizes a flexible and human - rather than a
rigid process- or tool-oriented - approach to defining product strategy and
carrying out work. Teammates focus heavily on customer feedback to make
improvements and adjust roadmaps throughout the product management process.
This creates more responsive teams, leads to quicker iterations, and creates a
more lovable experience overall.
Benefits of agile product management
Agile redefines how product managers think about planning
and building products. Traditionally, new customer experiences were
planned, designed, implemented, and tested in a step-by-step way. This meant
that new functionality was delivered sequentially. Once requirements were
defined and handed off to the development team, it was difficult to make any
changes. The failure rate of large-scale and lengthy software development
projects drove the need for a more fluid approach. Teams needed a way to adapt
to customer feedback and other learnings.
Agile provides a more flexible approach than traditional
software planning and development. Products are built in short increments,
giving product managers the opportunity to adjust the plan along the way. Here
are some of the key benefits of agile product management:
- Learn
from customers throughout the product lifecycle
- Continuously
adjust the near-term roadmap to meet customer needs
- deliver
value to customers in an incremental way
- Respond
to new and changing requirements
- Collaborate
with engineering to quickly deliver work
Agile product management practices
Being a product manager in an agile environment requires
flexibility. This is because less time is spent defining the product upfront,
so product managers must continuously adapt the product roadmap
and reprioritize what to build based on customer feedback.
Here is an overview of how the core product management
responsibilities are carried out in an agile environment:
Set product strategy
Setting a clear strategy is crucial in an agile environment.
Product managers are responsible for defining the product vision and
long-term direction. This requires working closely with customers to understand
their pain points, researching the market, and setting
strategic product goal and initiatives that align with overall
business objectives.
Understand customer needs
Agile methodologies focus on delivering value to customers
quickly. This means product managers must stay close to customers to understand
exactly what they want. One tenet of agile is gathering
feedback early and often to ensure the product delivers the expected
benefits to users.
Create the product roadmap
An agile roadmap sets a near-term plan for
achieving the product strategy. It typically represents monthly or quarterly
commitments and is adjusted regularly to accommodate change. Product
managers build the roadmap around strategic themes of work that
maintain the overall vision and deliver meaningful value to customers.
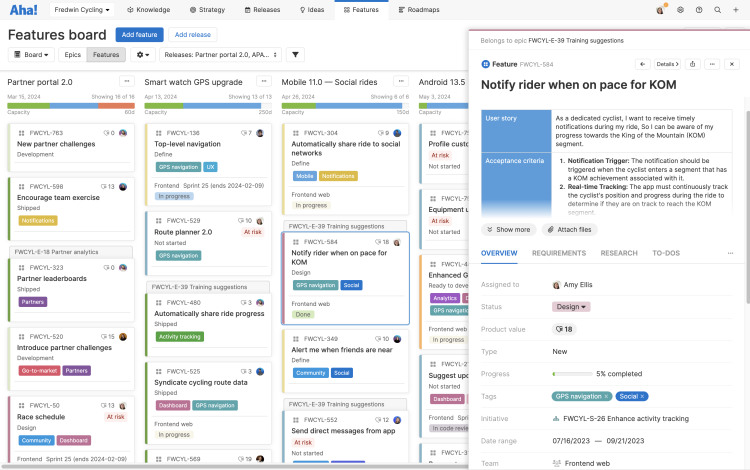
Prioritize features
Agile product management involves continuously
prioritizing features for implementation — maintaining
the product backlog, defining user stories, and deciding what to
build and when. Product managers work closely with engineers to estimate
features, define requirements, and collaborate on a release
plan based on the team’s capacity.
Release customer experiences
Agile teams strive to frequently deliver new customer
experiences. The cadence can vary from quarterly to monthly, weekly, or even
daily. Regardless of the frequency, product managers are responsible for
delivering a Complete Product Experience (CPE) to customers. This
involves working closely with engineering, IT, marketing, sales, and support to
ensure organizational readiness.
Measure product success
Product success in an agile environment is measured by how
customers interact with products and services and the impact on customer
acquisition, growth, and retention. Measures of success include customer
engagement (such as time in product and returning users), conversion rates,
customer churn, and the frequency of feature updates.
Roles and responsibilities in agile product management
Agile methodologies introduce a number of additional roles
to structure how team work together. Since we already described the core
responsibilities of a product manager in agile, let’s look at some of the other
roles that are explicitly defined in the scrum framework.
Development team An agile development
team is a cross-functional and self-organized group of people that have
the necessary skills to produce a working, tested increment of a product. The
team often includes skills such as design, development, testing, and delivery.
Product owner A product owner is
responsible for maximizing the value of the product created by the development
team. This internal-facing role gathers technical
requirements, refines the product backlog, and details user
stories.
Scrum master The scrum master is a
servant-leader who is responsible for coaching the team in agile
practices. This role guides the team through the agile process to complete
the work the product owner prioritizes. Scrum masters remove impediments that
keep the team from doing their work.
Stakeholders can be anyone affected by the
development of a software project. This includes a broad category of people,
such as end users, executives, IT, operations, portfolio managers, and
support.
Product manager vs. product owner
It is important to understand that these are roles rather
than job titles. This can create confusion about the differences between a
product manager and a product owner. In reality, the product manager is the
product owner. This is because the responsibilities of a product owner
fundamentally cover the internal-facing work a product manager does — working
closely with engineering to build new customer experiences.
Some organizations choose to break out product management
work into two roles. In this situation, the product manager assumes an external
focus, while the product owner details user stories and participates
in scrum rituals. Both roles are important to the overall success of
a product and must work closely together to build products that customers love.
The table below explains how the responsibilities of a
product manager and product owner differ when they are discrete roles:
|
Responsibility |
Product manager |
Product owner |
|
Define the product vision and set the long-term direction |
X |
|
|
Conduct market and competitive research |
X |
|
|
Work closely with customers, prospects, and partners to
capture their needs |
X |
|
|
Build the near-term product roadmap |
X |
|
|
Prioritize and score features based on customer and
business value |
X |
|
|
Communicate the product vision and business intent to the
development team |
X |
|
|
Lead technical requirements gathering, consulting with
internal stakeholders |
X |
|
|
Refine the product backlog, breaking
down epics and estimating user stories. |
X |
|
|
Attend scrum meetings including sprint planning,
standups, and retrospectives |
X |
|
|
Document user story details, create mockups, and
work with UX on design |
X |
|
|
Document new features for implementation |
X |
|
|
Support non-technical teams (sales, marketing, support) |
X |
|
|
Write acceptance criteria |
X |
X |
|
Attend iteration demos |
X |
X |
|
Demonstrate the latest iterations to customers and gather
feedback |
X |
X |
Agile product management tools
As you have learned in this guide, agile product management
requires a specific way of thinking and working. There are many
tools you can use to help you carry out your core product management
responsibilities in an agile way. Here are a few of the most common ones.
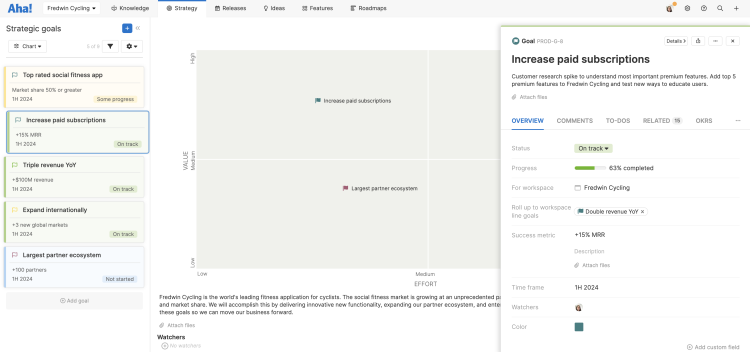
Goal matrix
Setting measurable, time-bound goals helps product
managers prioritize features that deliver strategic value. Use a matrix to
visualize your goals so everyone understands the “why” behind your product
decisions.
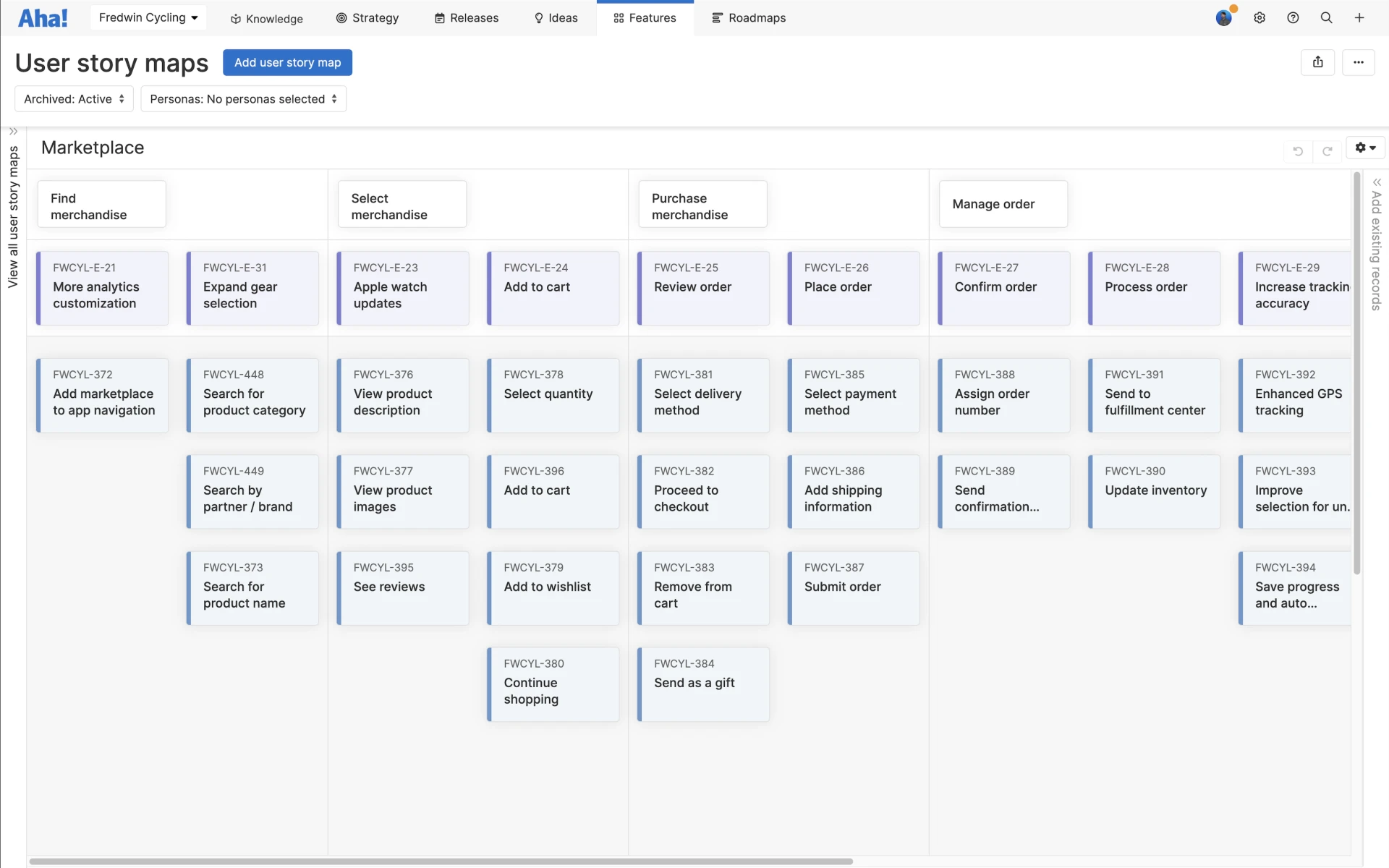
User story maps
User story maps give you a way to visualize work based on what your customer is trying to do.
This helps you prioritize the user stories
that deliver the most value for customers.