Tomcat is a
free and open-source web server. It was developed at Sun Microsystems (an
American technology company, currently acquired by Oracle). Tomcat is the
implementation of Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) in the newer version of
Jakarta Package (Jakarta EE). It supports Jakarta Servlet, Jakarta Server Page,
Jakarta Expression Languages, Jakarta WebSockets, etc. It provides a “JAVA
HTTP” web server.
What is
Tomcat?
Apache
Tomcat is an open-source web server and also a servlet container that is
developed by the Apache Software Foundation. It helps in implementing the Java
serverlets, Java serverpages, and other Java-based web technologies. It allows
the developers in running the java applications on a web server. It is widely
used for hosting the java applications due to its reliability, scalability and
strong performance in handling the dynamic web content.
How to
Install Apache Tomcat and Setup the Environment?
The following are the steps that helps in guiding how to install the apache tomcat in windows and setup its environment:Step 1: First, you have to download the Windows Service Installer from their official website using the Windows Tomcat Binary Distribution.
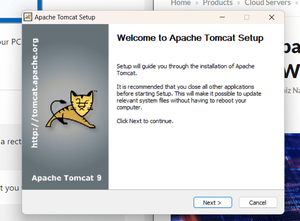
Step 2: The following screenshot
illustrates on the setup of tomcat, it will go through asking for value
definition regarding setup.
Step
3: You need to
click on next button.
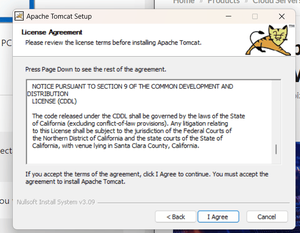
Step 4: Then agreed for installation.
Step 5: Then next -> next->
Finish.
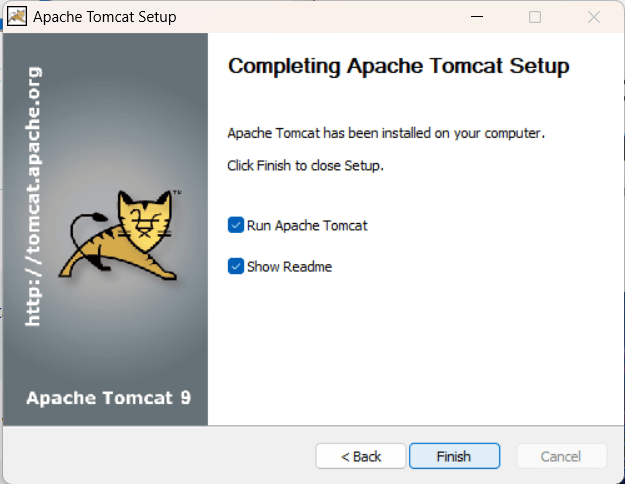
Step
6: Now Your
server is running on port “http://localhost/8080″.
.png)
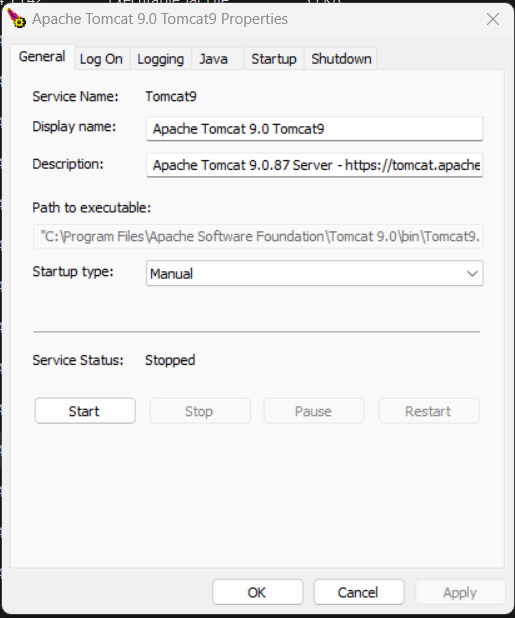
Restart
or Running of Tomcat Server
If you want
to stop the server then you need to go to the folder name “Program Files” like
in my system “C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation” >> “C:\Program
Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 9.0\bin”.
Step 1: Then go inside bin folder
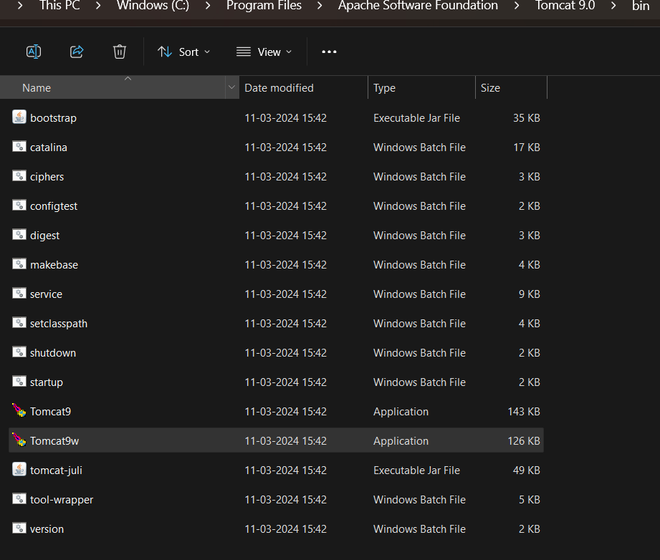
Step
2: Right click
on Tomcat9 and then click on stop and similar you can again re-start from here.
How to install Tomcat Server on Linux? A Step-By-Step Guide
The
following steps guides you on how to install the tomcat server on Linux:
Step 1: Install Java (if not already installed) on using the following command in the terminal.
sudo apt updateStep
2: Install the
default JDK (Java
Development Kit) with the following command execution.
sudo apt install default-jdkStep
3: Verify
whether the Java installation has done successfully or not through the below
command.
java -version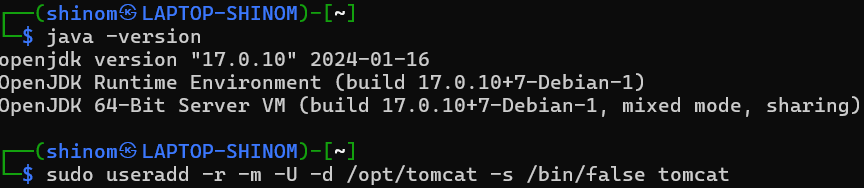
Setting up a
Tomcat User
The
following steps guide you on how to setup the tomcat user:
Step 1: Create a new user with the new
user name with useradd command as follows:
sudo useradd -r -m -U -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/false tomcatStep
2: Downloading
the Tomcat package
with the below command:
wget -c https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.87/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.87.tar.gzStep 3: After the downloading extract the
file with tar command as follows:
sudo tar xf apache-tomcat-9.0.87.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcatStep 4: Change directory
cd /opt/tomcat
ls -ls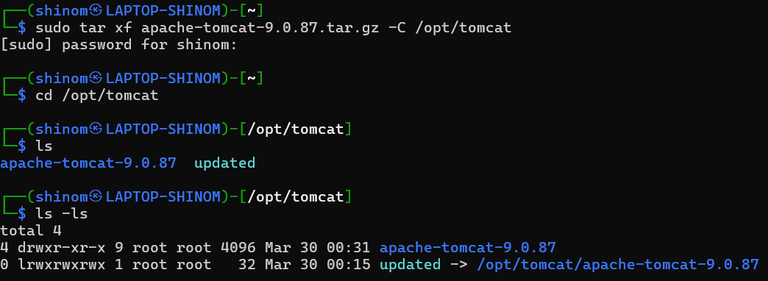
Steps To
Change The Bin Directory
The
following steps help in changing the bin directory of tomcat:
Step 1: Change to root user
sudo suStep 2: Change directory
cd /opt/tomcat/apache-tomcat-9.0.87/bin/
Step
3: Start Tomcat
using either of the following commands
sh startup.sh
OR
./startup.shStep 4: Open browser, now server is
running on
http://localhost:8080/.png)
Step 5: For stop running server
./shutdown.sh
Advantages
Of Apache Tomcat
The
following are the advantages of apache tomcat:
- Open Source: Tomcat comes
as free to use and with having large community support.
- Light Weight: It requires
only fewer resource in compared to full-fledged application servers. It is
ideal for the small to medium sized applications.
- High Comptability and
Integration: It provides fully compatible with java EE
specifications, supporting java servlets JSP and web socket technologies.
- Security and Stability: It
provides the security features and regular updates, ensuring a stable and
secure production environment.
Disadvantages
Of Apache Tomcat
The
following are the disadvantages of apache tomcat:
- Slower Performance Under Heavy
Load: When the server experiences high traffic, Tomcat’s performance
may slow down.
- Limited Technical Support: The
availability of technical support for Tomcat is limited compared to
commercial alternatives.
- LImit Features: It lacks
some advanced features that found in the comprehensive application
servers, such as built-in enterprise services, advanced clustering and
extensive management tools.
- Complex Configuration: While
setuping the straightforward, configuring the tomcat for advanced features
helps in optimizations.
Applications
of Apache Tomcat Server
The
following are the some of the applications of the tomcat server:
- Web Hosting for Java
Applications:
- Tomcat is widely used for
hosting Java-based applications on the web.
- It implements the Java Servlet
and JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications.
- Embedded Servers:
- Tomcat can be embedded within
other applications or services.
- Developers often use it as an
embedded servlet container for lightweight deployments.
- Commonly used for enterprise
applications involving:
- Java Expression Language
- Java Servlet
- Java WebSockets
- Java Server Pages2
- Web Applications Deployment:
- Each web application comprises
resources such as HTML with
Java code, Server Pages, Java Servlets, libraries, and other items
required to execute the program.
- These web applications are
stored in Tomcat’s “webapps” directory as folders or WAR (Web
Application Archive) files
Trouble Shooting Issues with Tomcat Server
The following are the some of the tomcat server trouble shooting issues:
1. Checking Log Files
- Action: Review the `catalina.out`,
`localhost`, and `manager` log files located in the `logs` directory.
- Purpose: Logs provide detailed
error messages and stack traces that can help identify the root cause of
issues, such as configuration errors, deployment problems, or runtime
exceptions.
2. Validating Configuration Files
- Action: Ensure that the
`server.xml`, `web.xml`, and `context.xml` configuration files are
correctly formatted and properly configured.
- Purpose: Misconfigurations in these
files can lead to startup failures, incorrect application behavior, or
security vulnerabilities. Validate XML syntax and configuration settings
to resolve such issues.
3. Monitoring Resource Usage
- Action: Use monitoring tools to check
CPU, memory, and disk usage on the server running Tomcat.
- Purpose: High resource usage can
cause performance degradation and slow response times. Identifying
resource bottlenecks allows for appropriate scaling or optimization
measures, such as adjusting JVM settings or load balancing.
4. Diagnosing Network Issues
- Action: Test network connectivity
and port accessibility using tools like `telnet` or `netstat`.
- Purpose: Network problems can prevent clients from connecting to the Tomcat server. Ensure that the server is listening on the correct ports and that there are no firewall or security group rules blocking access.
- Web Hosting for Java
Applications:


No comments:
Post a Comment