MongoDB is a powerful and flexible solution for handling modern data needs. As a leading NoSQL database, MongoDB offers a dynamic schema design, enabling developers to store and manage data in a way that aligns seamlessly with contemporary application requirements.
Unlike
traditional relational databases, MongoDB’s document-oriented architecture
allows for greater agility and scalability, making it a preferred choice
for businesses and developers aiming to handle large volumes of unstructured or
semi-structured data.
In this
article, we will explore the key features of MongoDB, its advantages over
traditional databases, and how it can be leveraged to optimize data management
in various applications.
What is
Mongo-DB?
MongoDB is
an open-source document-oriented database that is designed to store a large
scale of data and also allows you to work with that data very efficiently. It
is categorized under the NoSQL (Not only SQL) database because the storage and
retrieval of data in the
MongoDB are
not in the form of tables.
The MongoDB
database is developed and managed by MongoDB. Inc under SSPL(Server Side Public
License) and initially released in February 2009. It also provides
official driver support for all the popular languages like C, C++, C#, and
.Net, Go, Java, Node.js, Perl, PHP, Python, Motor, Ruby, Scala, Swift, Mongoid.
So, that you can create an application using any of these languages. Nowadays
there are so many companies that used MongoDB like Facebook, Nokia, eBay,
Adobe, Google, etc. to store their large amount of data.
Working of
MongoDB
MongoDB is a
database server and the data is stored in these databases. Or in other
words, MongoDB environment gives you a server that you can start and then
create multiple databases on it using MongoDB.
Because of its NoSQL Database, the data is stored in the collections and
documents. Hence the database, collection, and documents are related to each
other as shown below:
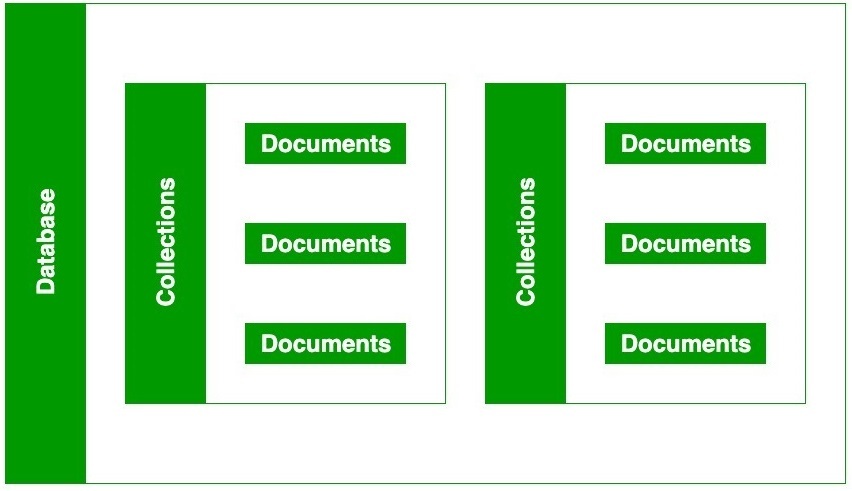
- The MongoDB database contains
collections just like the MYSQL database contains tables. You
are allowed to create multiple databases and multiple collections.
- Now inside of the collection we
have documents. These documents contain the data we want to store in the
MongoDB database and a single collection can contain multiple documents
and you are schema-less means it is not necessary that one document is
similar to another.
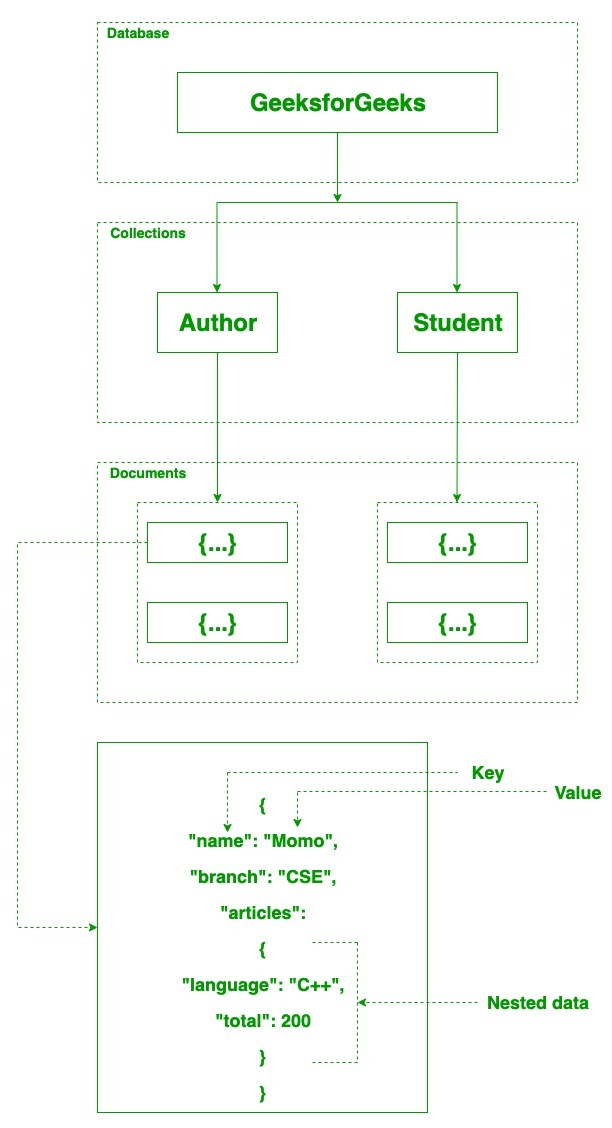
- The documents are created using
the fields. Fields are key-value pairs in the documents, it is just like
columns in the relation database. The value of the fields can be of any
BSON data types like double, string, boolean, etc.
- The data stored in the MongoDB
is in the format of BSON documents. Here, BSON stands for Binary
representation of JSON documents. Or in other words, in the backend, the
MongoDB server converts the JSON data into a binary form that is known as
BSON and this BSON is stored and queried more efficiently.
- In MongoDB documents, you are
allowed to store nested data. This nesting of data allows you to create
complex relations between data and store them in the same document which
makes the working and fetching of data extremely efficient as compared to
SQL. In SQL, you need to write complex joins to get the data from table 1
and table 2. The maximum size of the BSON document is 16MB
NOTE: In MongoDB server, you are allowed to run multiple databases.
For example: we have a database named GeeksforGeeks. Inside this database, we have two collections and in these collections we have two documents. And in these documents we store our data in the form of fields. As shown in the below image:
- The MongoDB database contains
collections just like the MYSQL database contains tables. You
are allowed to create multiple databases and multiple collections.
Difference
between MongoDB and RDBMS ?
Some major
differences in between MongoDB and the RDBMS are as follows:
|
MongoDB |
RDBMS |
|
It is a non-relational and
document-oriented database. |
It is a relational database. |
|
It is suitable for hierarchical data
storage. |
It is not suitable for hierarchical
data storage. |
|
It has a dynamic schema. |
It has a predefined schema. |
|
It centers around the CAP Theorem (Consistency,
Availability, and Partition tolerance). |
It centers
around ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and
Durability). |
|
In terms of performance, it is much
faster than RDBMS. |
In terms of performance, it is slower
than MongoDB. |
Features
of MongoDB
- Schema-less Database: It is the great feature provided
by the MongoDB. A Schema-less database means one collection can
hold different types of documents in it. Or in other words, in the
MongoDB database, a single collection can hold multiple documents and
these documents may consist of the different numbers of fields, content,
and size. It is not necessary that the one document is similar to
another document like in the relational databases. Due to this cool
feature, MongoDB provides great flexibility to databases.
- Document Oriented: In MongoDB, all the data
stored in the documents instead of tables like in RDBMS. In these
documents, the data is stored in fields(key-value pair) instead of rows
and columns which make the data much more flexible in comparison to RDBMS.
And each document contains its unique object id.
- Indexing: In MongoDB database, every
field in the documents is indexed with primary and secondary indices this
makes easier and takes less time to get or search data from the pool of
the data. If the data is not indexed, then database search each
document with the specified query which takes lots of time and not so
efficient.
- Scalability: MongoDB provides
horizontal scalability with the help of sharding. Sharding means
to distribute data on multiple servers, here a large amount of data is
partitioned into data chunks using the shard key, and these data chunks
are evenly distributed across shards that reside across many physical
servers. It will also add new machines to a running database.
- Replication: MongoDB provides high
availability and redundancy with the help of replication, it creates
multiple copies of the data and sends these copies to a different server
so that if one server fails, then the data is retrieved from another
server.
- Aggregation: It allows to perform
operations on the grouped data and get a single result or computed result.
It is similar to the SQL GROUPBY clause. It provides three
different aggregation i.e, aggregation pipeline, map-reduce
function, and single-purpose aggregation methods
- High Performance: The performance of MongoDB is
very high and data persistence as compared to another database due to its
features like scalability, indexing, replication, etc.
Uses of
MongoDB
MongoDB is a
popular NoSQL database known for its flexibility, scalability, and performance.
It is widely used in various applications across different industries. Here are
some common uses of MongoDB:
- 1. Content Management
Systems (CMS): MongoDB’s flexible schema and powerful query
capabilities make it an ideal choice for content management systems. It
can efficiently handle diverse content types and structures, enabling
dynamic and scalable content management solutions.
- 2. E-commerce Platforms:
E-commerce platforms benefit from MongoDB’s ability to store and retrieve
large amounts of product data quickly. Its flexible schema supports
dynamic product catalogs, user profiles, shopping carts, and transaction
histories.
- 3. Real-Time Analytics:
MongoDB is well-suited for real-time analytics applications due to its
high-performance data ingestion and querying capabilities. It can handle
large volumes of data in real-time, making it ideal for monitoring, fraud
detection, and personalized recommendations.
- 4. Internet of Things
(IoT): IoT applications generate vast amounts of data from sensors and
devices. MongoDB’s scalability and flexible data model allow it to
efficiently store and process this data, enabling real-time analysis and
decision-making for IoT systems.
- 6. Gaming Applications:
Gaming applications generate complex data structures, such as player
profiles, scores, achievements, and game states. MongoDB’s document-based
model allows for efficient storage and retrieval of this data, supporting
high-performance gaming experiences.
- 7. Log Management and
Analysis: Organizations use MongoDB to store and analyze log data from
various sources. Its ability to handle large volumes of unstructured data
makes it ideal for logging, monitoring, and troubleshooting applications
and infrastructure.
- 9. Customer Relationship
Management (CRM): CRM systems use MongoDB to manage customer data,
interactions, and sales pipelines. Its ability to handle complex
relationships and unstructured data enables more personalized and
effective customer engagement strategies.
- 10. Social Networks:
Social networking applications require a database that can handle complex
relationships, user-generated content, and real-time interactions.
MongoDB’s flexibility and scalability make it an excellent choice for
building social networks and community platforms.
- 11. Big Data
Applications: MongoDB is used in big data applications for its ability
to store and process large volumes of diverse data types. It integrates
well with big data technologies like Hadoop and Spark, enabling advanced
data analytics and processing.
- 12. Healthcare Systems:
Healthcare applications use MongoDB to manage patient records, clinical
data, and medical images. Its flexible schema allows for the efficient
storage of complex healthcare data, supporting better patient care and
data analysis.
Advantages
of MongoDB
- It is a schema-less NoSQL
database. You need not to design the schema of the database when you are
working with MongoDB.
- It does not support join
operation.
- It provides great flexibility to
the fields in the documents.
- It contains heterogeneous data.
- It provides high performance,
availability, scalability.
- It
supports GeoSpecial efficiently.
- It is a document oriented
database and the data is stored in BSON documents.
- It also supports multiple
document ACID transition(string from MongoDB 4.0).
- It does not require any SQL
injection.
- It is easily integrated
with Big Data Hadoop
Disadvantages
of MongoDB
- It uses high memory for data
storage.
- You are not allowed to store
more than 16MB data in the documents.
- The nesting of data in BSON is
also limited you are not allowed to nest data more than 100 levels.
Conclusion
MongoDB is a
powerful and flexible NoSQL database that caters to the needs of modern
applications requiring scalable, high-performance data management. Its
schema-less design, horizontal scalability, and rich querying capabilities make
it a popular choice for developers and businesses alike. Understanding
MongoDB’s features and benefits can help organizations efficiently handle large
volumes of data and adapt to evolving requirements.


No comments:
Post a Comment