CICD are
essential practices in software development. In continuous integration the
system builds the code with every commit to the repository and stores the
artifacts into a storage space, further making them available for testing and
deployment processes. On the other hand continuous deployment automates the
deployment process enabling swift and consistent releases. This entire process
is important as it decreases the manual error and makes product deployment more
efficient and reliable.
AWS
CodePipeline simplifies this entire continuous integration and continuous
deployment process by automating the build, test, and deployment phases of the
software development process. Here in this article, I will walk through the
steps of how to integrate CodeBuild AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy with
AWS CodePipeline to automate the entire code commit, code build, and code
deploy stages in a continuous integration and continuous deployment process.
Steps To
Use AWS CodePipeline For Continuous Integration And Deployment
Step 1: First
create a CodeCommit repository.
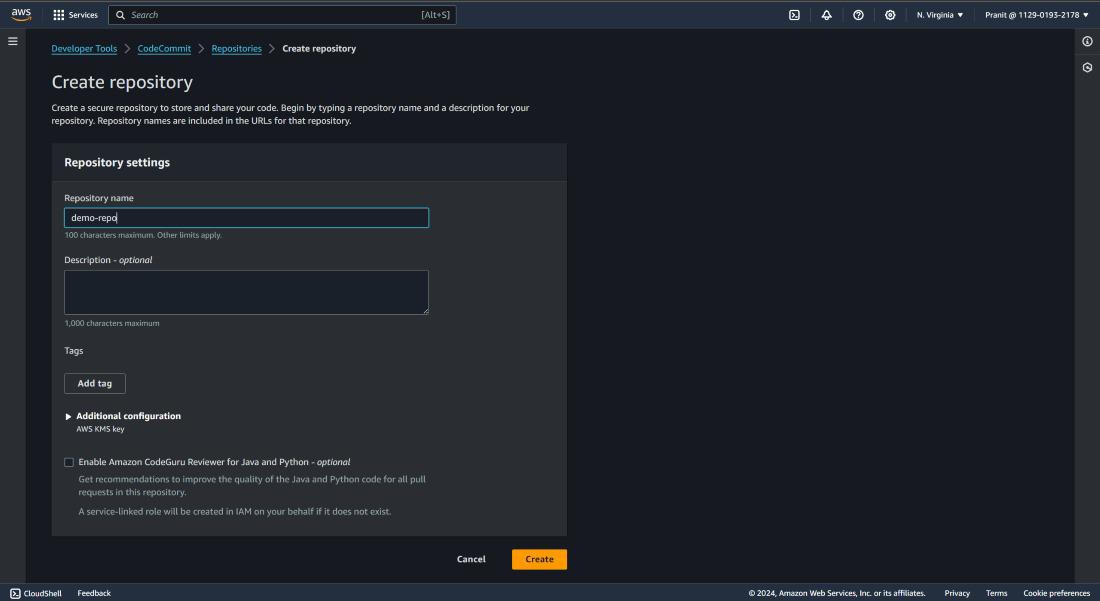
Step 2 : On the top right corner of page , click Clone URL to copy the HTTPS URL
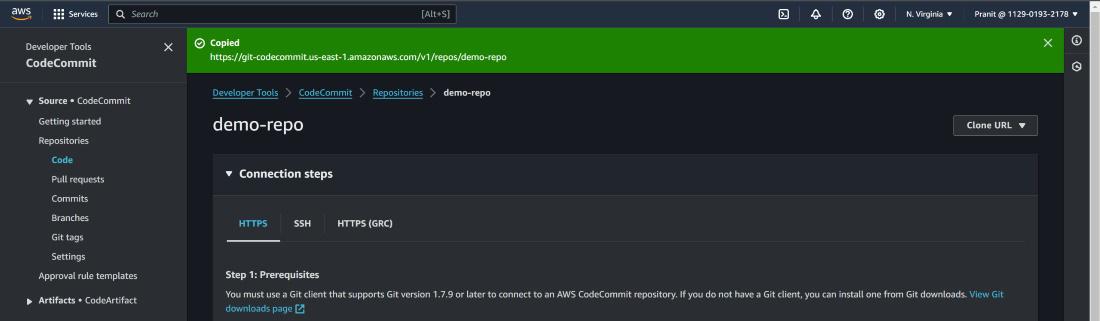
Step 3 : Now go to a local editor terminal
(for e.g. visual studio) and write the git clone using the copied URL . But
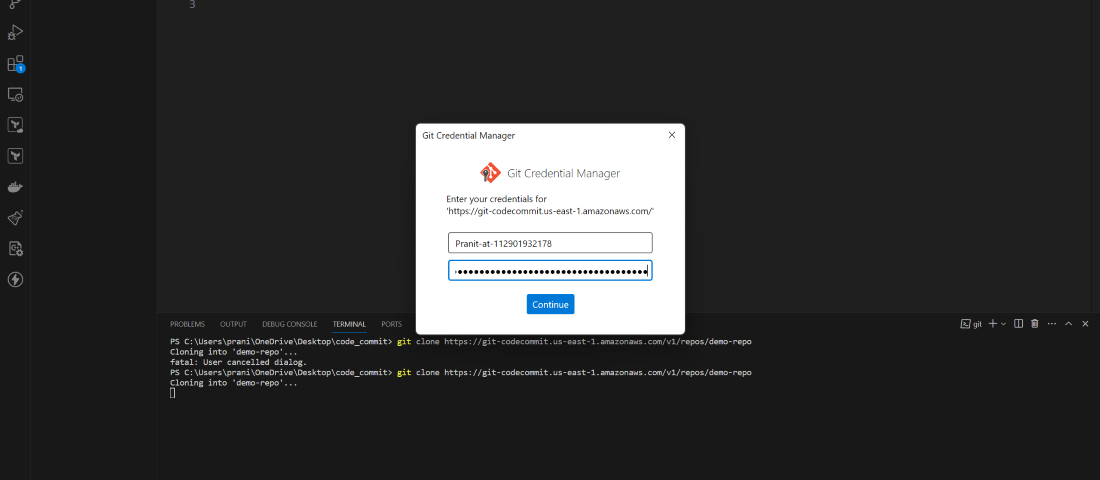
here you will see a new screen will pop out and it will be asking GIT
credential .
git clone <copied URL>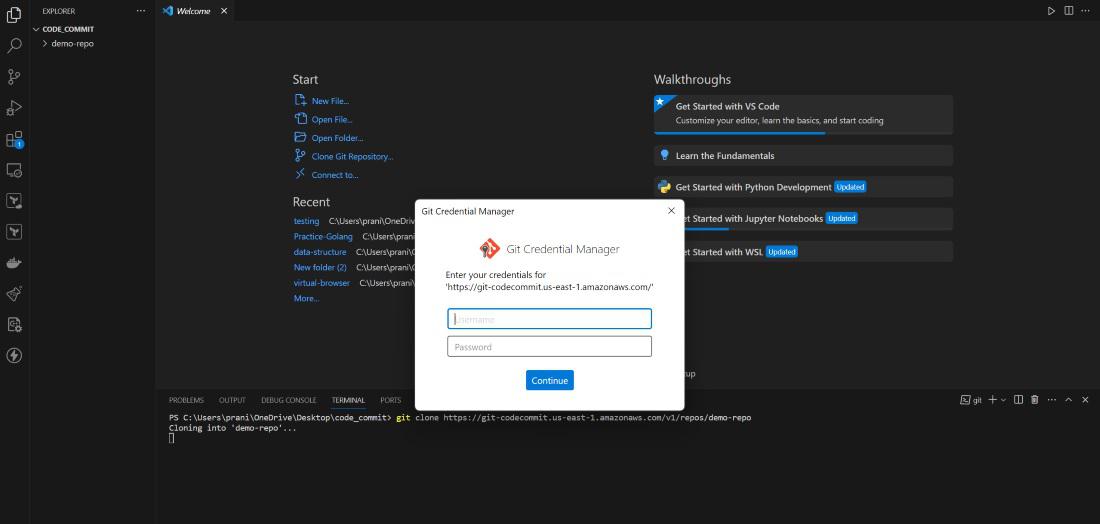
Step 4 : Now to generate GIT credential , go to the IAM service . Here go to the IAM user account that you are using using now . There you will find Security Credential, select that and scroll down to HTTPS GIT credentials for AWS CodeCommit . Here click Generate credentials.
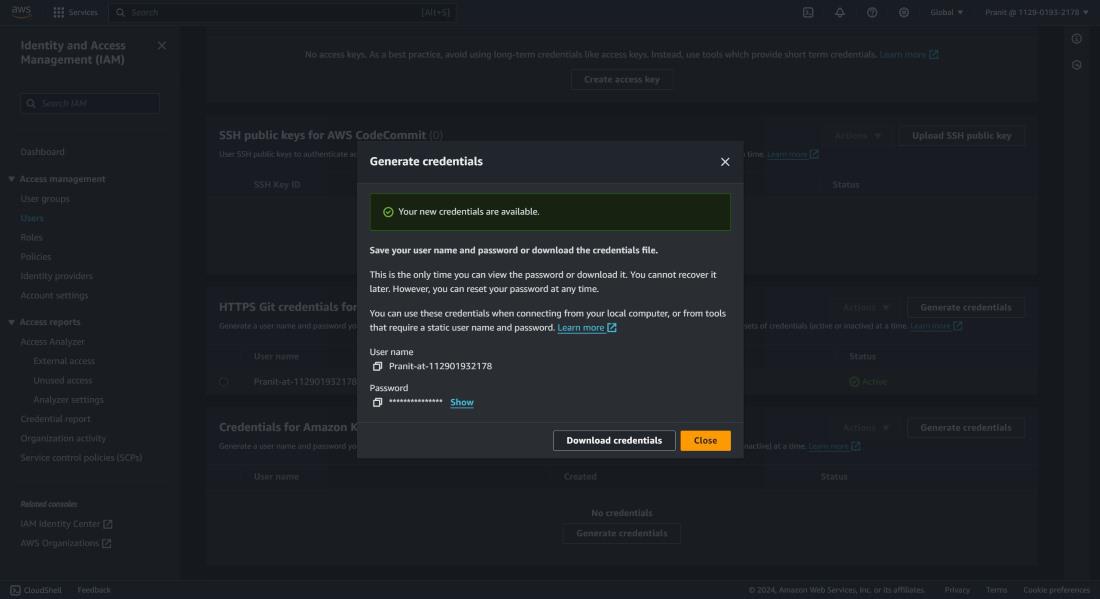
Step 5 : Now we have the GIT credentials . So
we can now git clone using the HTTPS URL of CodeCommit repository (the same
command used in step 3) . You can now successfully clone the repository
after entering the GIT credentials .
Step 6 : Now go inside the repository and
create a index.html . Basically here all the changes are in local environment ,
so to make sync the changes with the CodeCommit repository you need to push
all changes to the master branch of CodeCommit repository.
git add .
git commit -m "first commit in codecommit" (you can give any message inside the inverted commas)
git push origin master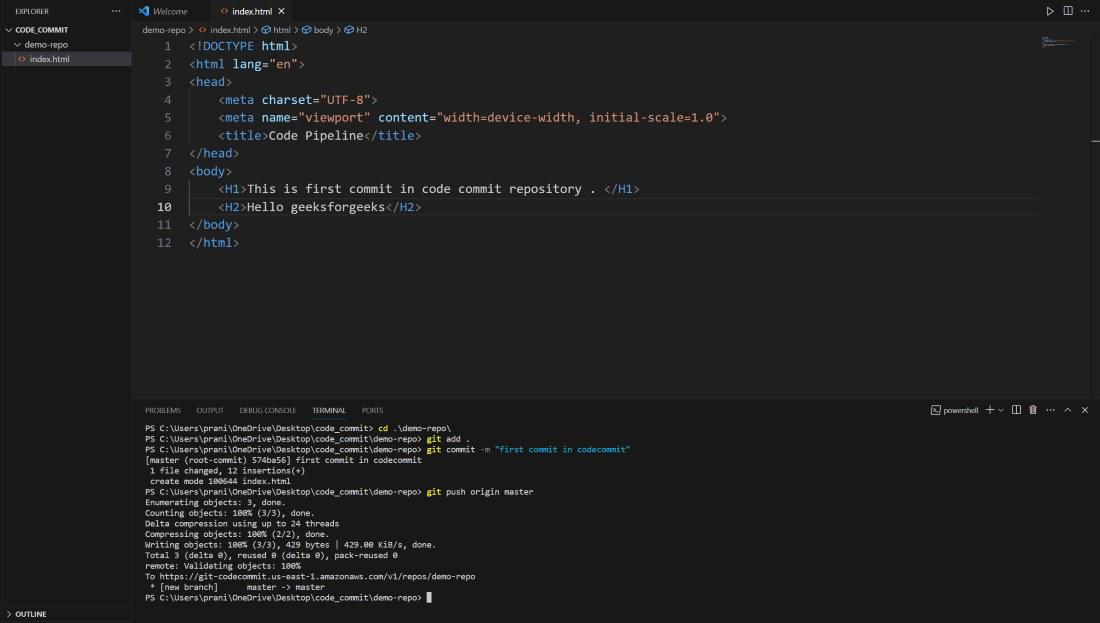
Step 7 : Now we have all these code present
inside the CodeCommit repository . We need to build these code now . Before
using AWS CodeBuild , we need a buildspec.yml file inside the
repository . This buildspec.yml defines the set of build commands and settings
which is necessary for providing a structured way to specify how CodeBuild
should build and package your application . Create a buildspec.yml file and push
it CodeCommit repository .
version : 0.2
phases:
install:
commands:
- echo Start with NGINX install
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get install nginx -y
build:
commands:
- echo Building...
- cp index.html /var/www/html/
artifacts:
files:
- /var/www/html/index.html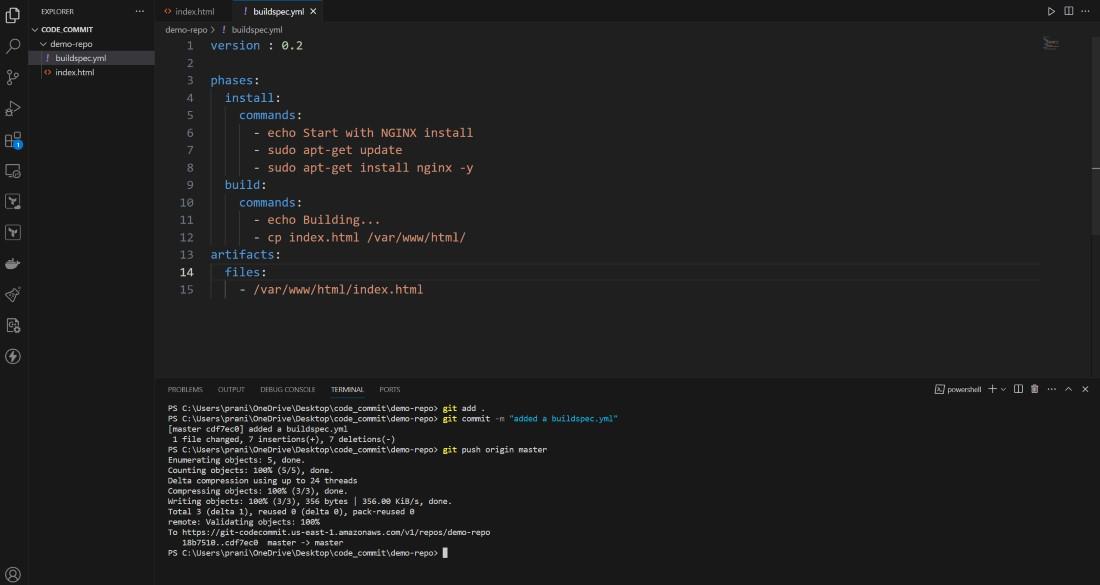
Step 8 : Now go
to AWS CodeBuild and create a build . Here provide the project name . Add CodeCommit as
code source and here also mention the branch you are using . Select Ubuntu as
operating system , standard runtime and use the latest image .
Here automatically a new service role will be created and attached to the build
. Mention the build file ,but if you have already selected buildspec.yml then
then there is no need for mentioning in the Buildspec name . Select no
artifacts . Here you can untick the Cludwatch logs and create the build .
Step 9 : After creating code build you can
start the build to see whether your build is successful or not . This build is
creating some artifacts which needs to be stored . So select edit and then
select artifacts .
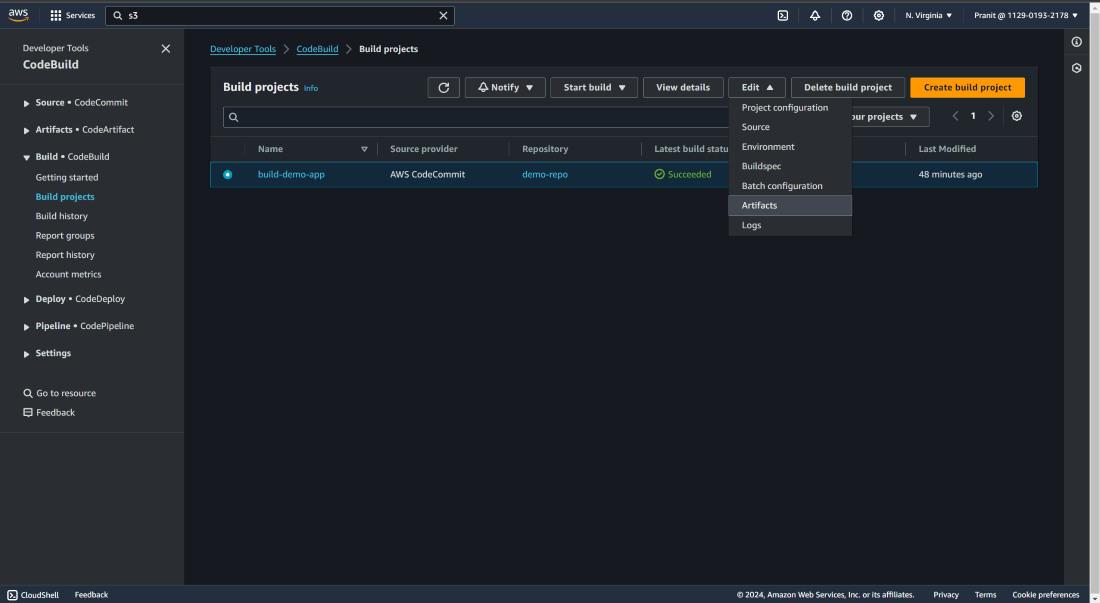
Step 10 : Here I have used Amazon S3 bucket to
store the artifacts . Mention the s3 bucket previously created here and in
names write artifacts.zip (<any-name>.zip)
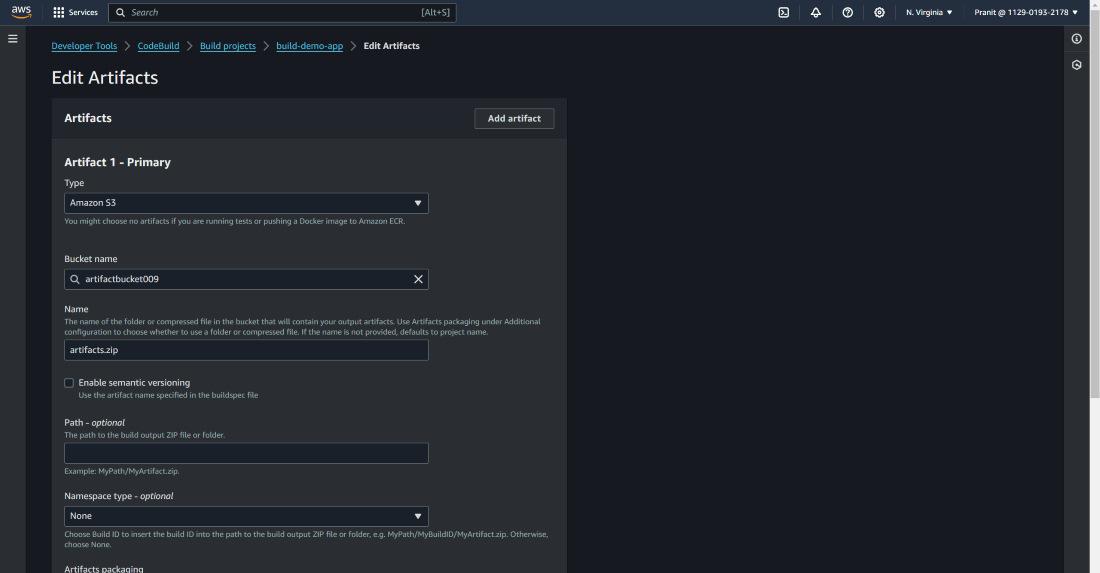
Step 11 : Then start the build . You can check
the phase details status .
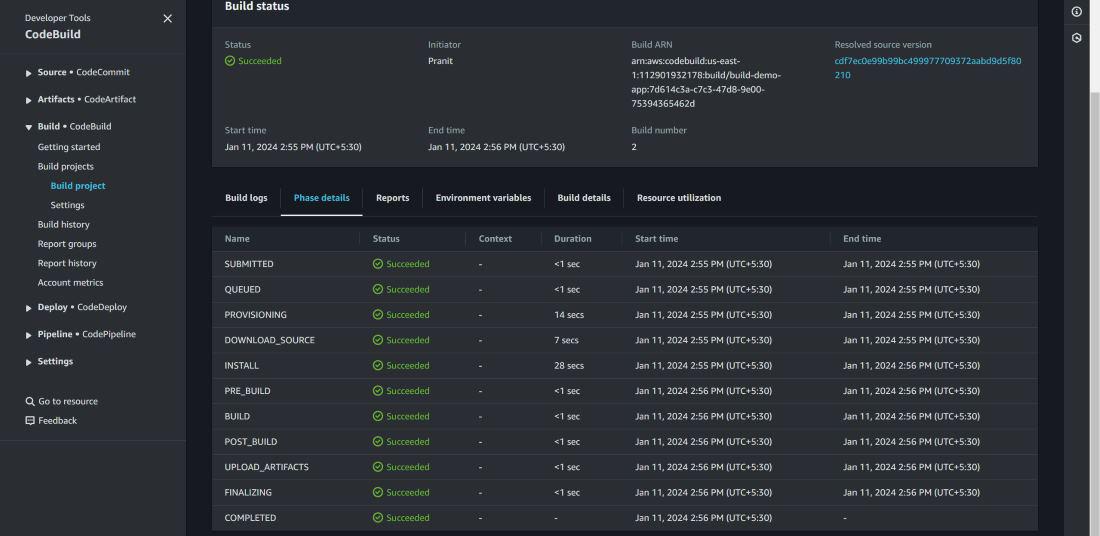
Step 12 : After build status is successful ,
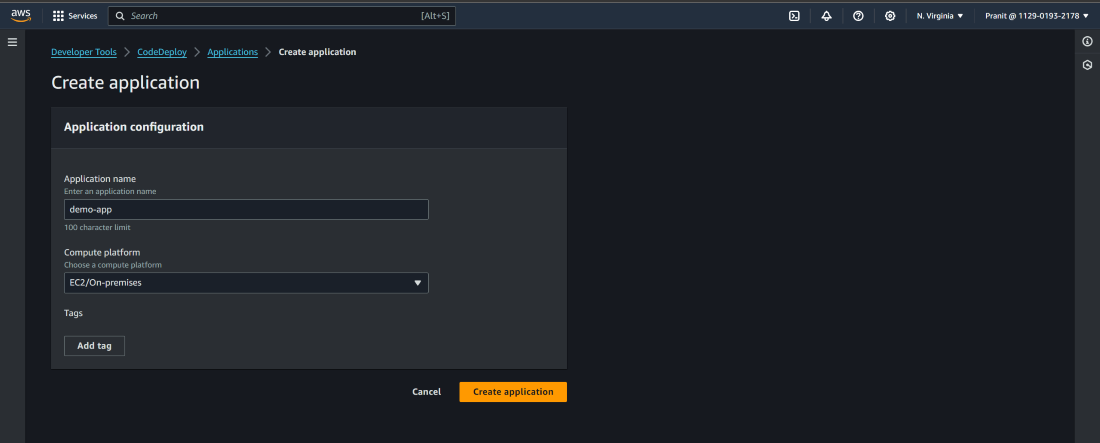
now we have to deploy our website . Create an application on AWS
CodeDeploy . Here mention the application name and select EC2/On-premises as
compute platform.
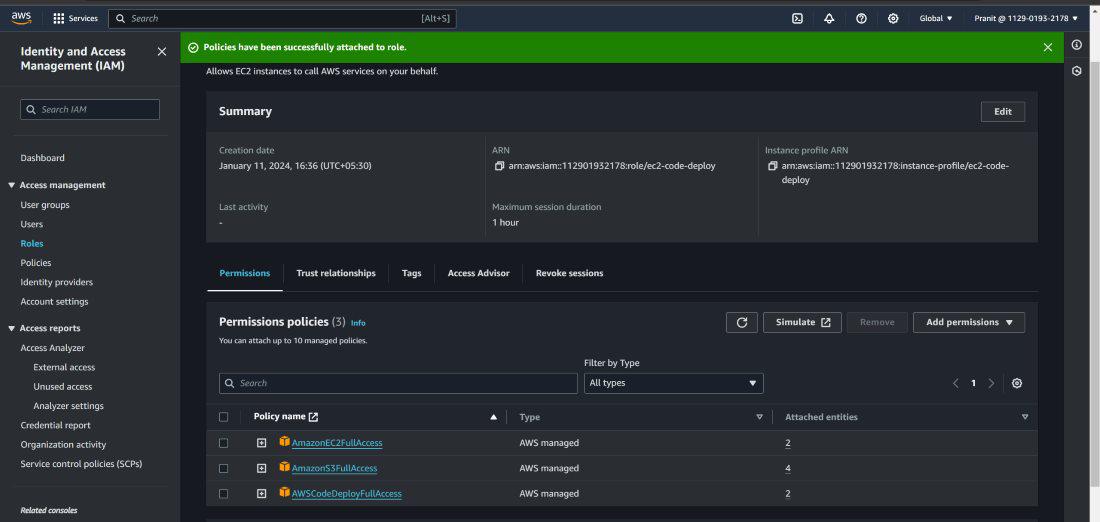
Step 13 : In the previous step we have taken
EC2 as compute platform . So now we have to create an EC2 instance. This
EC2 instance needs is used as deployment platform which is interacting with AWS
S3 bucket , AWS CodeDeploy service . So after creating EC2 instance you have
to create a IAM role and attach the role to the EC2 instance with
some policies AmazonEC2FullAccess , AmazonS3FullAccess and AWSCodeDeployFullAccess .
Step 14 : Create another IAM role for
deployment group with the policies AmazonEC2FullAccess , AmazonS3FullAccess , AWSCodeDeployFullAccess , AmazonEC2RoleforAWSCodeDeploy , AWSCodeDeployRole and AmazonEC2RoleforAWSCodeDeployLimited .
This role will attach to the deployment group that we will create in the next
step .
.jpg)
Step 15 : Now go to AWS CodeDeploy and create a
deployment group . Here mention deployment group name , attach the IAM role you
have created in the previous step , select EC2 for environment configuration
and attach the EC2 instance created in step 13 . And here we will
install codedeploy agent manually and so select never in install
codedeploy agent .
Step 16 : Now we have to install the codedeploy
agent on EC2 instance . You can install the codedeploy by following the
official documentation of AWS or you can directly install codedeploy agent
using the following script (make sure that you are using us-east-1 or else
you have change the region name in the script) :
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ruby-full ruby-webrick wget -y
cd /tmp
wget https://aws-codedeploy-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/releases/codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_all.deb
mkdir codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_ubuntu22
dpkg-deb -R codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_all.deb codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_ubuntu22
sed 's/Depends:.*/Depends:ruby3.0/' -i ./codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_ubuntu22/DEBIAN/control
dpkg-deb -b codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_ubuntu22/
sudo dpkg -i codedeploy-agent_1.3.2-1902_ubuntu22.deb
systemctl list-units --type=service | grep codedeploy
sudo service codedeploy-agent status
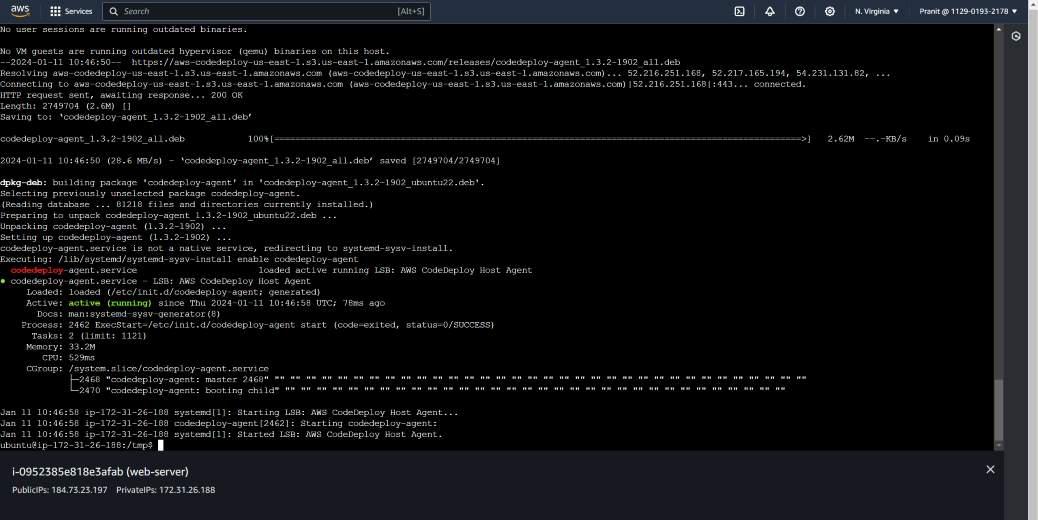
Step 17 : Like CodeBuild stage , CodeDeploy
stage also needs a configuration file called appspec.yml which
provides instructions to CodeDeploy on how to deploy your application . Create
appspec.yml in the local environment .
version: 0.0
os: linux
files:
- source: /
destination: /var/www/html
hooks:
AfterInstall:
- location: scripts/install_nginx_service.sh
timeout: 300
runas: root
ApplicationStart:
- location: scripts/start_nginx_service.sh
timeout: 300
runas: rootHere there
are two scripts used , one script install the nginx service and another script
to start the nginx service .
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y nginxstart_nginx_service.sh
#!/bin/bash
sudo service nginx startAfter
creating all these files you have to push all the changes to AWS CodeCommit
repository .
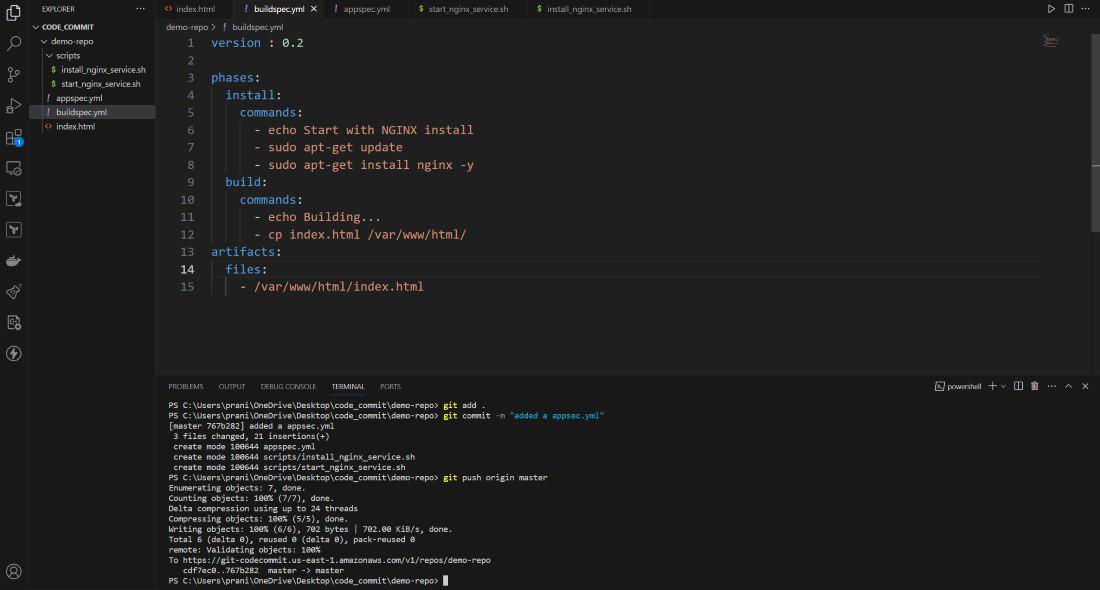
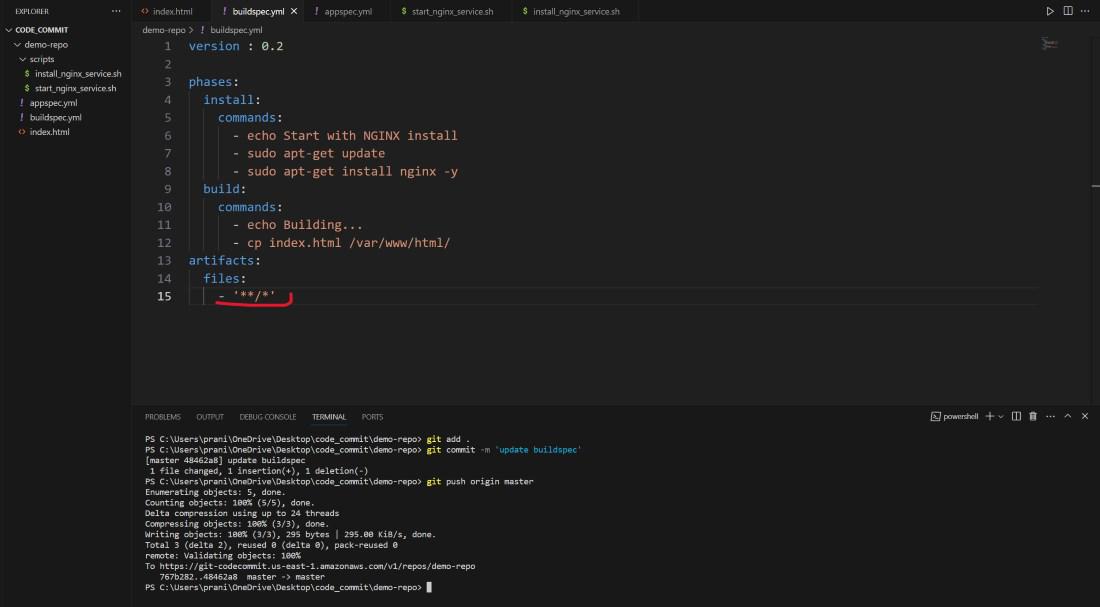
Step 18 : Now you need to update the
artifacts files in the buildspec.yml and then push the changes
to AWS CodeCommit repository .
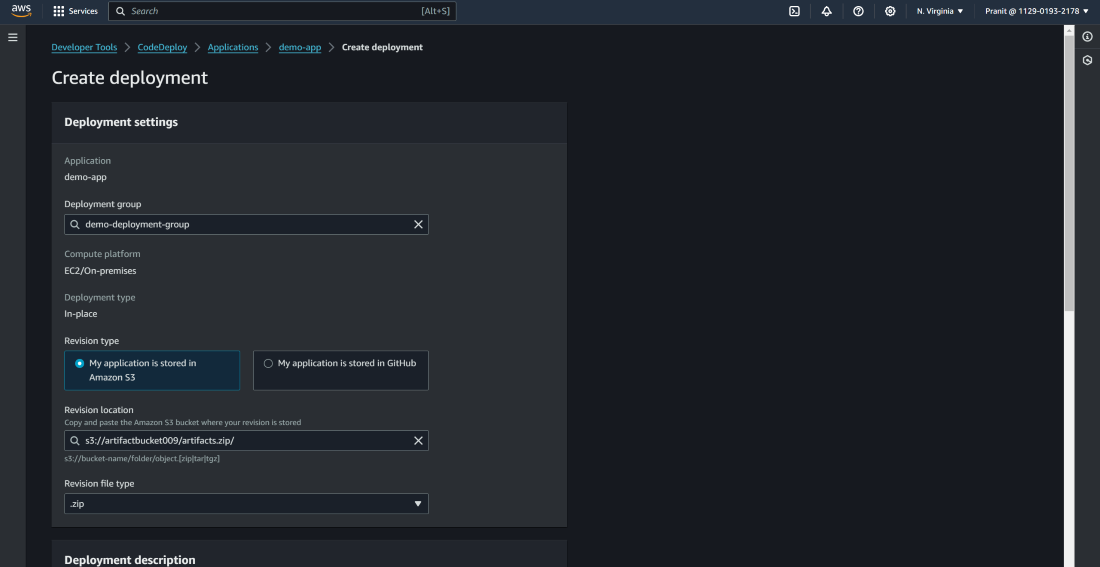
Step 19 : Now here we have to create a
deployment using revise location as S3 Bucket's URL . Previously we
have used artifacts.zip to store the artifacts in S3 bucket , so mention the
revision file type as .zip .
Step 20 : After this check the CodeCommit
repository if all the files are present or not . Now again start the codebuild
and then create the deployment .
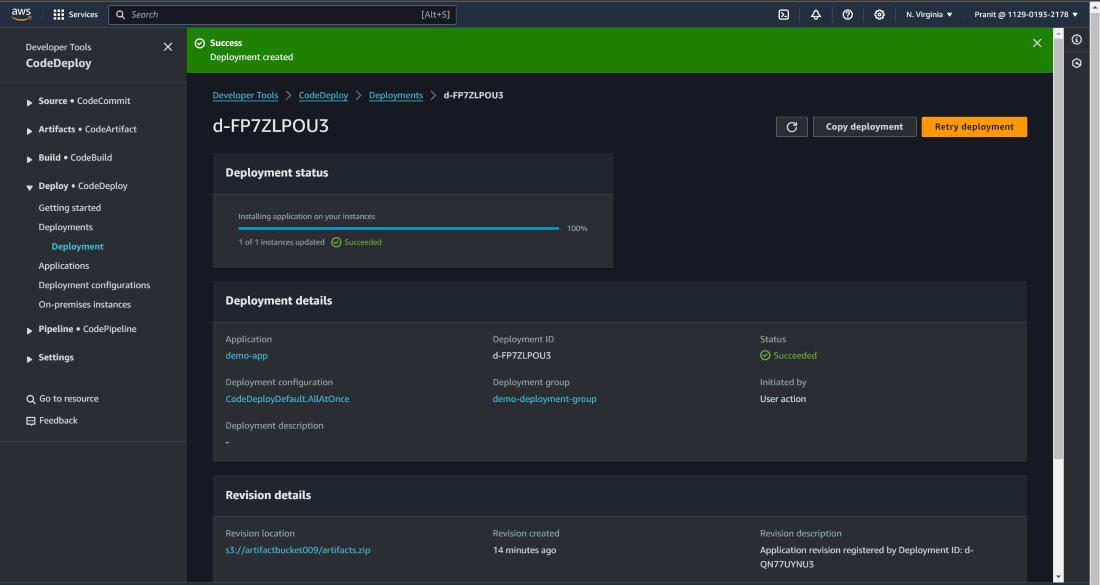
Step 21 : After the successful deployment then
access the Public IP of EC2 instance to access the webpage .
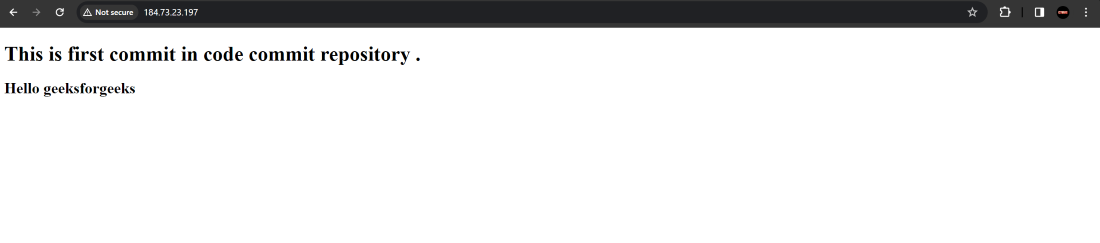
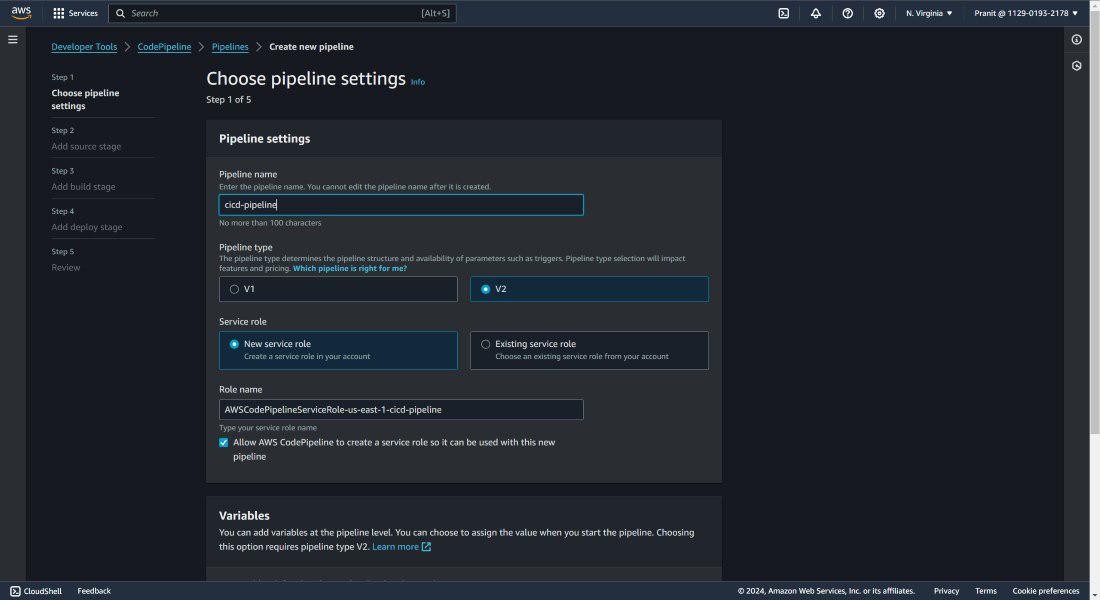
Step 22: Till now all the above steps are done
manually . To automate the CodeCommit , CodeBuild and CodeDeploy stage we need
to use AWS CodePipeline . So create an AWS CodePipeline .
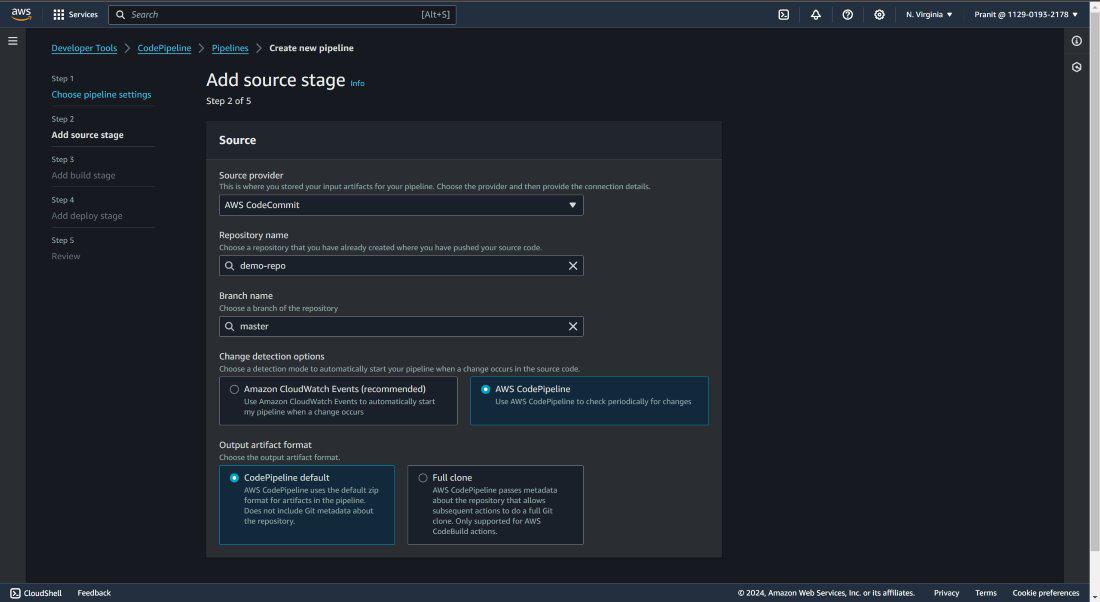
Step 23 : Select code source as AWS CodeCommit
and mention the repository name and branch also . Here choose AWS CodePipeline in
Change detection options (After selecting this it will automatically detect
changes in the repository and start the code build, code deploy stage).
Step 24 : Select AWS CodeBuild as build
provider and enter the project name .
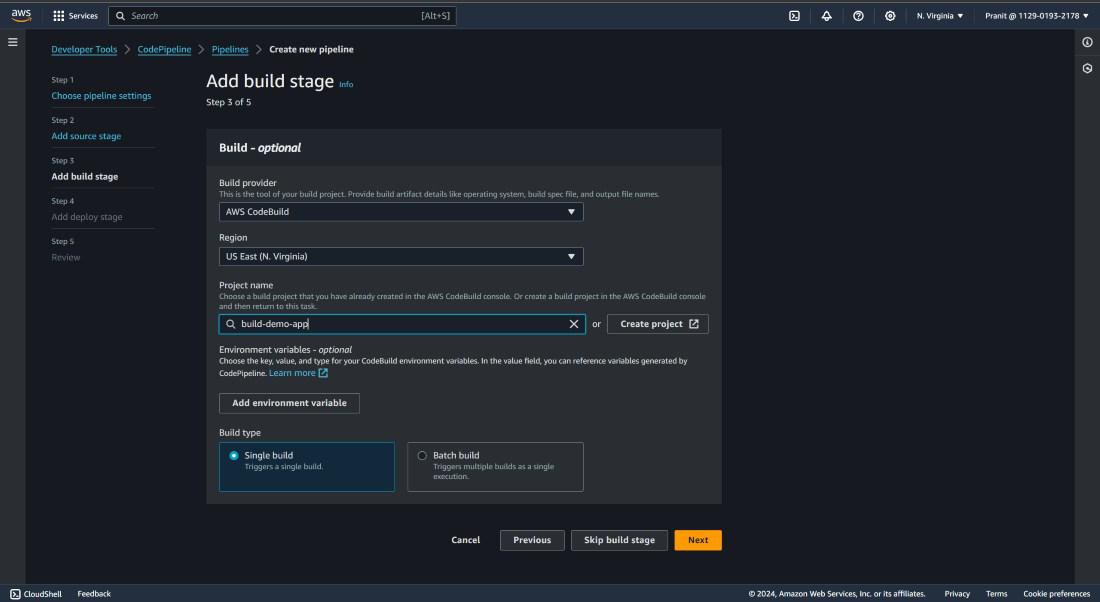
Step 25 : Here also mention the AWS CodeDeploy
as deploy provider and mention the application name and deployment group name .
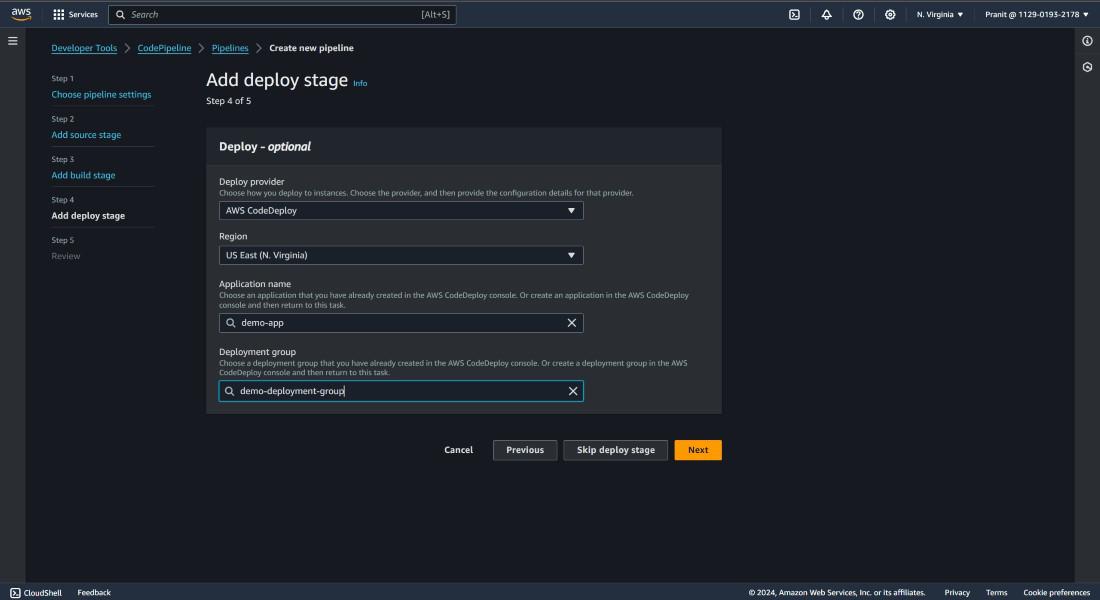
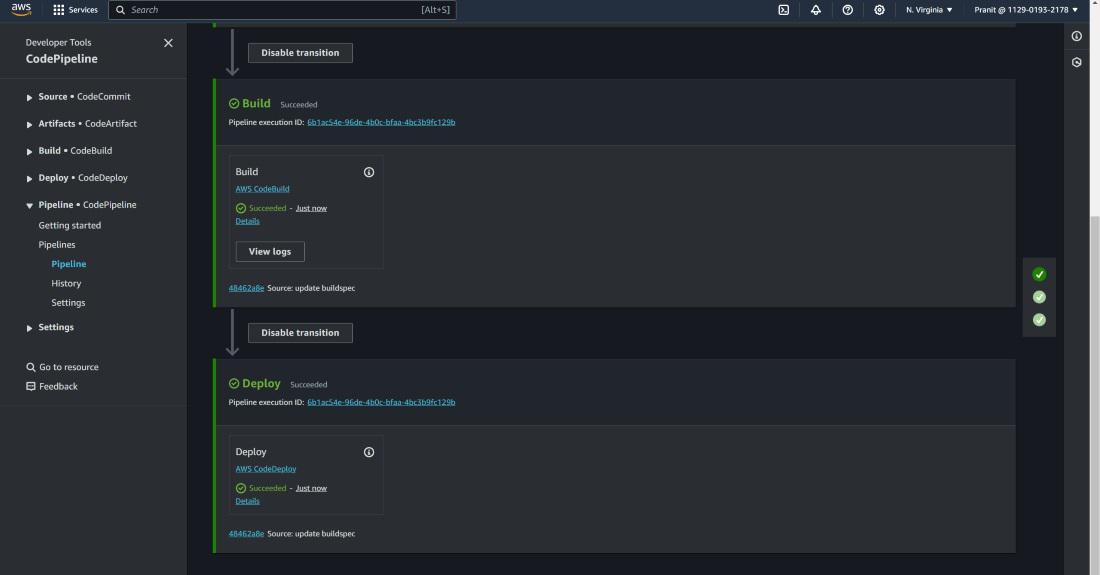
Step 26 : After this the pipeline will be
executed successfully .
Step 27 : Now access the webpage using the
Public IP of EC2 instance .
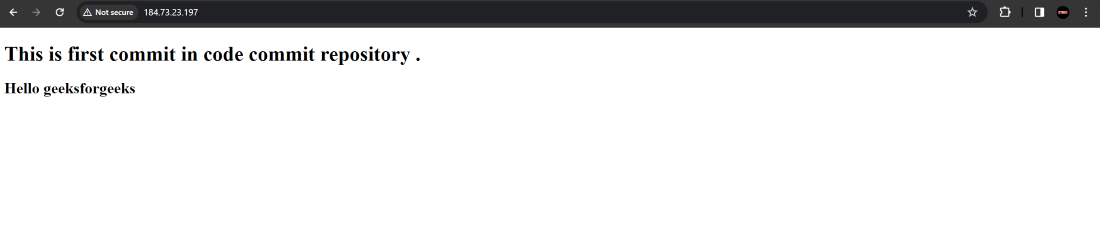
Step 28
: To check
whether the AWS CodePipeline working properly or not , make some changes in the
index.html and push the changes to the AWS CodeCommit repository .
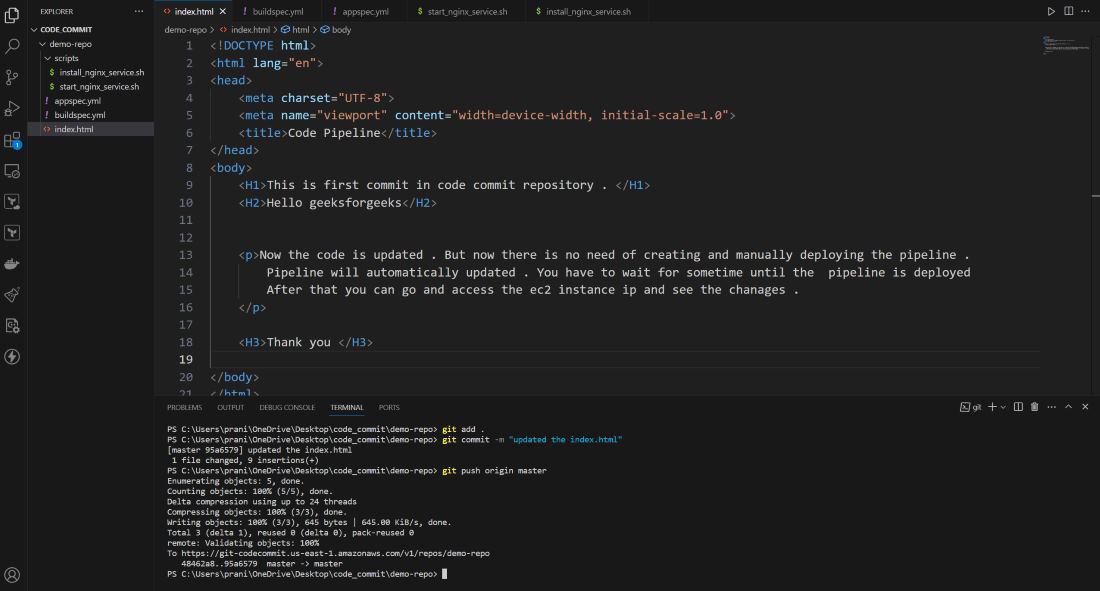
Step 29 : After changes are pushed to AWS
CodeCommit repository , you will notice that pipeline will automatically start
and can see the recent commit message also .
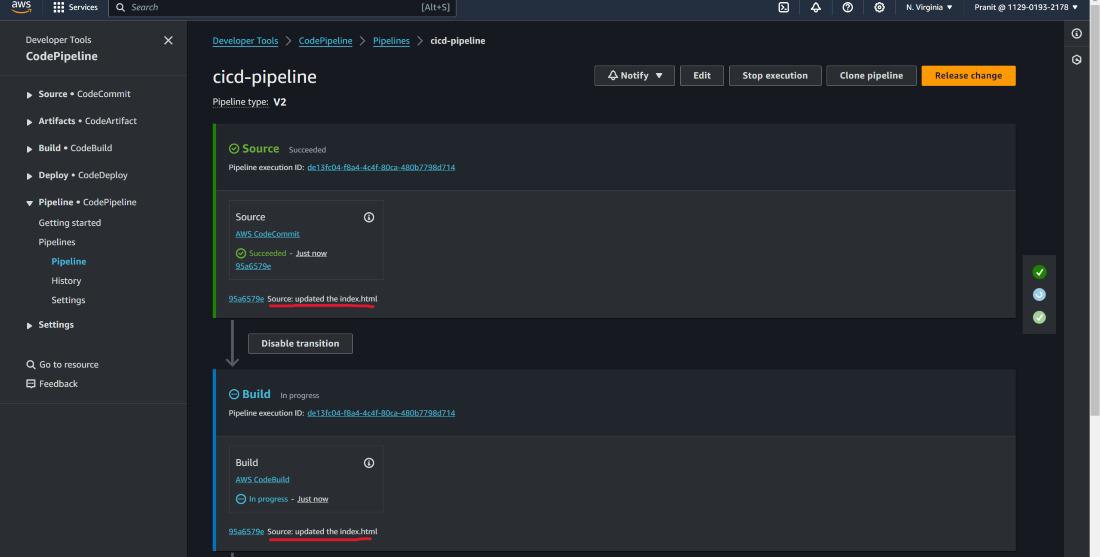
Step 30 : Finally access the updated webpage
using the Public IP of EC2 instance .
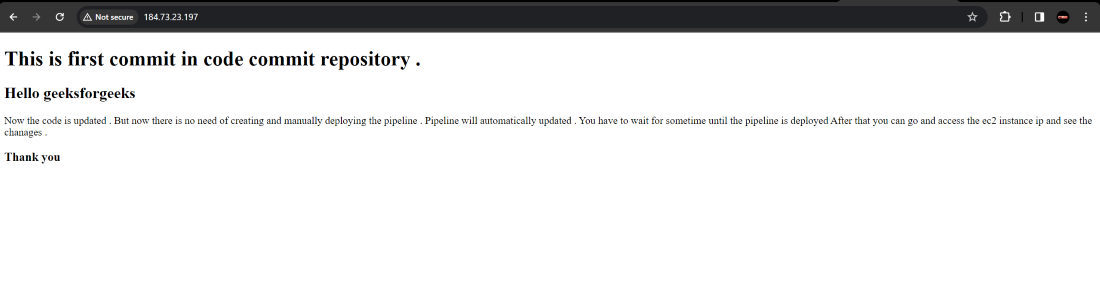
Conclusion
So you have
now learned why continuous integration and continuous deployment is important .
Also we have gone through the various steps to automate the different stages
like code commit , code build and code deploy using AWS CodePipeline . Finally
we successfully accessed the website using the Public IP of EC2 instance .
FAQS On
How to use AWS CodePipeline for continuous integration and deployment
1. What are
different source code repositories that can integrate with AWS CodePipeline ?
CodePipeline
integrates with different source code repositories such as AWS CodeCommit
, GitHub, Bitbucket ,S3 Bucket , etc .
2. How
execution of pipeline triggered in AWS CodePipeline ?
Pipeline
executions can be triggered manually , based on a schedule or automatically in
response to any change in the source code repository .
3. What are
artifacts ?
Artifacts
are deployable packages or build outputs that are produced during the pipeline
action .
4. How can
you troubleshoot any type of issues in AWS CodePipeline ?
Cloud
monitoring tools such as AWS cloudWatch logs
and CloudTrail can be used to find any type of issues in the AWS
CodePipeline .
5. Can AWS
CodePipeline integrate with third party tools ?
The answer is yes . For e.g AWS CodePipeline can integrate with Jenkins to build the code or it can also integrate with different source code repositories like Github , Bitbucket , etc .


No comments:
Post a Comment