Amazon RDS is a relational database management system along with the facilities of the AWS cloud platform. It facilitates us in creating database instances as per our requirements, i.e. resizable, variety of database types, etc.
What is
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)?
Amazon Web
Services offers Amazon RDS a service where it is managed completely by AWS and
also it offers wide range data base engines like the following:
1. MySQL
2.
PostgreSQL
3.
Oracle
4. MSSQL
The backup
of the data and the infrastructure will be taken care of by the AWS scaling and
balancing the load the security is very high the data will be encrypted at rest
can control the accesses to the data with the help of IAM. The Disaster
Recovery will automatically take by the AWS automatically by the AWS
How
Amazon RDS Works?
Traditionally,
database management used to be a very scattered service, from the webserver to
the application server and then finally to the database. For the maintenance of
such a vast system a team was required, to shrink this workforce, AWS came
across an amazing all-in-one service, RDS. The whole architecture of RDS
includes every aspect of the traditional management system, all in place. Thus,
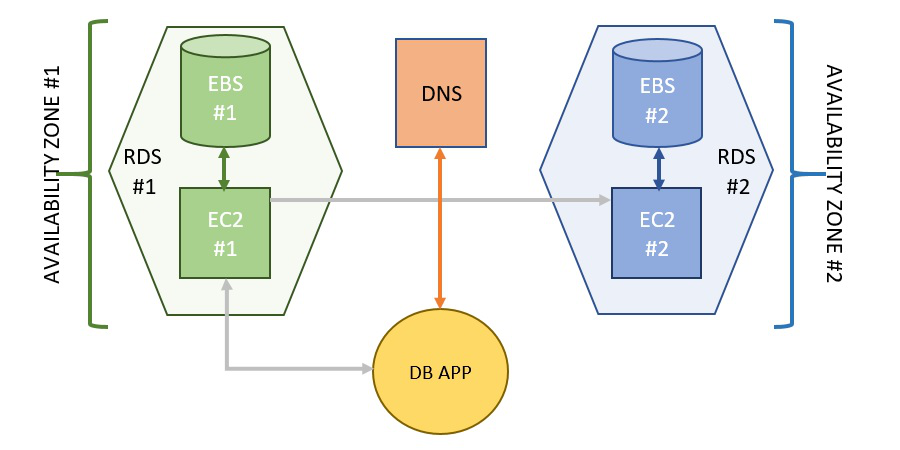
it includes everything from EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) to DNS
(Domain Name System). Every part of the RDS architecture has its own
separate set of features completely different from each other. A diagrammatical
representation of RDS has been attached ahead.
Use Cases
Of Amazon RDS (AWS)
Below are
some use cases of Amazon RDS mostly used for secured and highly configured
applications like gaming servers and health and financial applications.
- WebApplication: The Amazon RDS is mainly used
for the backend for web applications where it can support maximum no.of in
and output operation. And also is easy to scale up and down.
- Managed Database: Instead of you managing the
database AWS will provide Amazon RDS as a service by just doing some
configuration your database will be available to perform the operations.
- Isolation: You can integrate and configure
multiple applications with secure isolation by protecting the data of each
application’s customers while managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Highly Secured: You can use Amazon RDS for
domains like health care and banking because the data used in this type of
application is highly secure which can be achieved with the help of AWS
RDS.
Features
Of Amazon RDS
The
following are some key features of Amazon RDS:
- Availability: The “Automated Backup” feature
of RDS makes the recovery of the database instance much easier and makes
it available for access quickly. Other than that, “Database
Snapshots” are user-driven backup features initiated by Amazon
RDS, which makes it easier for the user to monitor all the alterations
made on the Database Instance. These snapshots can be
shared among multiple AWS accounts in order to expand the availability
of the DB instance, along with maintaining the security of the
confidential data.
- Security: While creating a new
database, you have to create a password that is totally restricted and
known to you only. And by default, you are given the “Admin
role” which has the maximum authority on that particular
database. Amazon RDS also allows its users to encrypt the databases
using “keys” which is managed by KMS (Key
Management Service) under Amazon RDS.
- Backups: RDS provides us the
facility to have backups. We can have backups in multiple forms. Snapshots are
basically non-editable backups used for maintaining records. We also can
create Automated Backups simply by altering the
configurations during creating the database. Reserved instances are
also another type of backup facility available here.
- Scalability: RDS enables us to automatically
scale up or scale down depending upon the number of transactions happening
on your database per minute. We can do both “Horizontal Scaling” and “Vertical
Scaling”. Let us go through the difference between both of them.
- Horizontal Scaling deals with scenarios where the
amount of traffic is increased on your database exponentially, in such
cases, this scaling comes into the picture. This simply creates multiple
hardware & software which are look-alike of the previously existing
ones on the cloud in order to tackle the traffic.
- Vertical Scaling deals with situations, where
the traffic is not very much increased but the current configurations of
the hardware & software are not able to handle the demands of the
client anymore. Using this scaling method, we are capable of adding
additional storage and processors to our pre-existing resources.
- Performance: RDS gives two SSD-backed storage
options for its users, i.e. General Purpose &
Provisioned. All these variants directly impact the level of
performance of the resource and its attached services. The general SSD is
very cost-effective and is used at places where a broad workforce is
required. Provisioned, as the name suggests are designed for temporary or
lower workloads purposes.
- Pricing: RDS only asks you to pay for
what you use, once you are done with a certain resource delete it and
don’t pay for it anymore. There is no compulsory minimal charge decided
for using RDS. Depending upon the Database Engines and
the type of database, a bill is calculated and sent to you at the end of
the month. For free tier accounts, special configurations are bound to
choose and you won’t get any bills if you delete all the resources you
used before logging out.
Amazon
RDS Alternatives
- MySQL – It is the 2nd most preferred
open-source RDBMS in the world. It is developed by Oracle. It is
not typically cloud-based in nature like Amazon RDS, i.e. it can be used
on PC as well. It is also offered as one of the options on RDS to choose
as Database Engine. It supports five server operating systems. The main
application of MySQL is in the e-commerce domain, data warehouse, and
logging application.
- PostgreSQL – It is one of the oldest RDBMS.
It is also one of the popularly used open-source RDBMS. It was developed
by PostgreSQL Global Development Group in 1989. It is a
cross-platform software, and it supports more operating systems as
compared to others. Its primary focus is maintaining the security of the
data and it is a vast kingdom of user-defined functions.
- MariaDB – It is the most compatible RDBMS,
and it supports both secondary database models, i.e. Spatial &
Graph. It was released in 2009, by MariaDB Corporation
Ab (MariaDB Enterprise). It supports a wide range of programming languages
and also allows users to introduce server-side scripts. One of the best
features of MariaDB is that it focuses on high-level security in the
community of MariaDB continuously finding and fixing the issues for
MariaDB.
All these
alternatives are found useful for users to meet their requirements at a certain
level. AWS introduced, RDS to ensure that the ultimate control resides in the
hands of the users. RDS is not of query-driven structure rather it is more like
a console in its structure.
Amazon
DynamoDB
DynamoDB
allows users to create databases capable of storing and retrieving any amount
of data and comes in handy while serving any amount of traffic. It dynamically
manages each customer’s request and provides high performance by automatically
distributing data and traffic over servers. It is a fully managed NoSQL
database service that is fast, predictable in terms of performance, and
seamlessly scalable. It relieves the user from the administrative burdens of
operating and scaling a distributed database as the user doesn’t have to worry
about hardware provisioning, patching Software, or cluster scaling.
Amazon
RedShift
It is a data
warehouse that is based on the cloud. Amazon Redshift has a commercial license
and is a part of Amazon’s web services. It handles large-scale of data and is
known for its scalability. It does parallel processing of multiple data. It
uses the ACID properties as its working principle and is very popular. It is
implemented in C language and has high availability.
Steps To
Configure Amazon RDS
Now, let us
look at the AWS Relational Database Service management console.
Step 1: To reach, the RDS management console. First login into your AWS account to create AWS free tier account . Once you are directed to the primary screen, at the leftmost part of it, click on “Services”. From the long list, look for the sub-heading “Databases” and under it, you will find “RDS”. Click on it. Here is the image to refer to.
Step 2: Once you tap on RDS, in a
while, you will be able to see the RDS management console. Refer to the image
attached ahead for a better understanding.
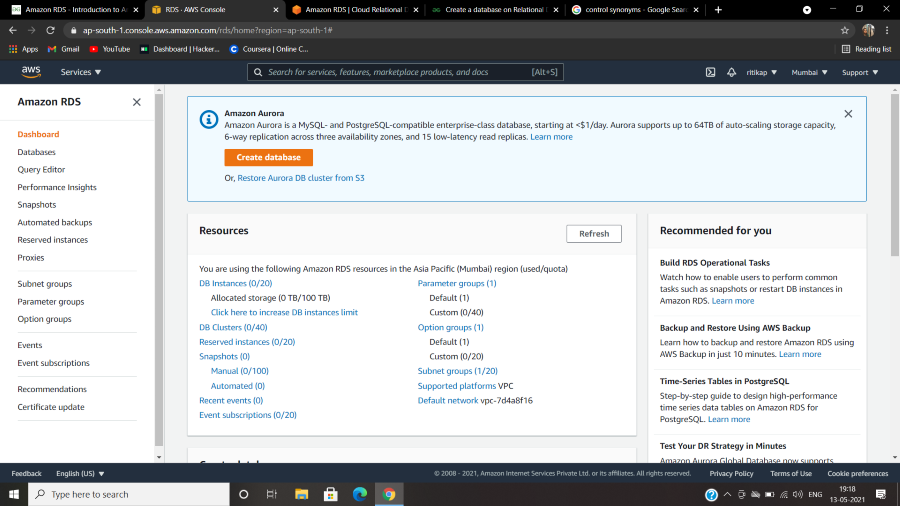
This is what
the RDS dashboard looks like. On the left, there is the navigation pane to
direct you to all the services under RDS. You can create your database from
here, by tapping on the orange box saying, “Create database”.
FAQs On
Amazon RDS
1. Is Amazon
RDS a Data Warehouse?
Database
servers in the cloud are managed by the Amazon Relational Database Service
(RDS). To access and analyse massive amounts of data, Amazon Redshift provides
data warehouse and data lake technologies.
2. What Type
Of Database Is RDS?
A managed
SQL database service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) is called Amazon
Relational Database Service (RDS).


No comments:
Post a Comment