AWS CodePipeline is a continuous delivery service you can use to model, visualize, and automate the steps required to release your software. You can quickly model and configure the different stages of a software release process. CodePipeline automates the steps required to release your software changes continuously.
What can I do with CodePipeline?
You can use CodePipeline to help you automatically build, test, and deploy your applications in the cloud. Specifically, you can:
Automate your release processes: CodePipeline fully automates your release process from end to end, starting from your source repository through build, test, and deployment. You can prevent changes from moving through a pipeline by including a manual approval action in any stage except a Source stage. You can release when you want, in the way you want, on the systems of your choice, across one instance or multiple instances.
Establish a consistent release process: Define a consistent set of steps for every code change. CodePipeline runs each stage of your release according to your criteria.
Speed up delivery while improving quality: You can automate your release process to allow your developers to test and release code incrementally and speed up the release of new features to your customers.
Use your favorite tools: You can incorporate your existing source, build, and deployment tools into your pipeline.
View progress at a glance: You can review real-time status of your pipelines, check the details of any alerts, retry failed stages or actions, view details about the source revisions used in the latest pipeline execution in each stage, and manually rerun any pipeline.
View pipeline history details: You can view details about executions of a pipeline, including start and end times, run duration, and execution IDs.
A quick look at CodePipeline
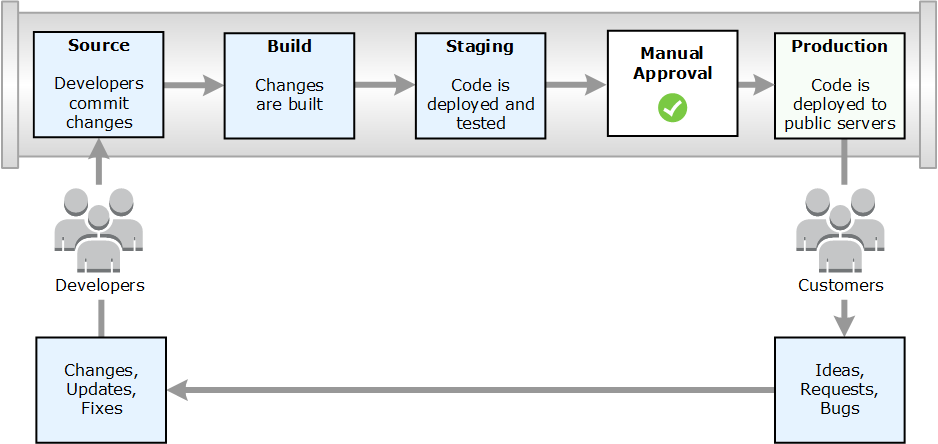
The following diagram shows an example release process using CodePipeline.
In this example, when developers commit changes to a source repository, CodePipeline automatically detects the changes. Those changes are built, and if any tests are configured, those tests are run. After the tests are complete, the built code is deployed to staging servers for testing. From the staging server, CodePipeline runs more tests, such as integration or load tests. Upon the successful completion of those tests, and after a manual approval action that was added to the pipeline is approved, CodePipeline deploys the tested and approved code to production instances.
CodePipeline can deploy applications to EC2 instances by using CodeDeploy, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, or AWS OpsWorks Stacks. CodePipeline can also deploy container-based applications to services by using Amazon ECS. Developers can also use the integration points provided with CodePipeline to plug in other tools or services, including build services, test providers, or other deployment targets or systems.
Let's deep dive in this with CLI tutorials:
A pipeline can be as simple or as complex as your release process requires.
Learn more about CodePipeline Concepts
Getting started with Pipeline here : Execution with example


No comments:
Post a Comment